Architecture
The K-A architecture is based on micro-services (mS). All components can be installed on different virtual machines (or pods), in an Intranet, or on a private Cloud, provided that all these machines are connected via TCP/IP, with exchange protocols allowed by IT policies.
The infrastructure of the K-A platform consists of Linux-based Opensource components that have been developed and/or used by IT giants. These components already operate for needs that are orders of magnitude higher than what is required for K-A, hence the certainty that they will not bottleneck if the right virtual hardware is assigned.
The most critical infrastructure component is Kubernetes (K8s), which orchestrates the platform and is generally pre-installed in Cloud installations. Kubernetes is the entry point for allocating and managing the platform resources; it also keeps the platform healthy and guarantees uninterrupted service.
The functional view below highlights the platform components — less the Linux infrastructure or the Kubernetes orchestrator.
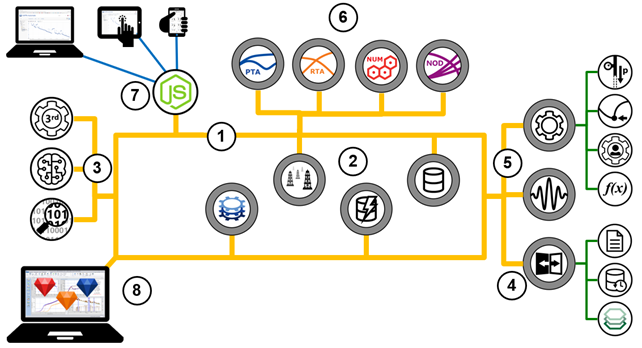
All microservices communicate through a bus (1) and expose public REST API.
Among the services are some KAPPA infrastructure micro-services (2), namely the Field service, the Data service, the Automation service, and the Event Store.
External applications, for instance AI or Data Analytics, can connect to the bus and consume the platform services APIs (3).
Access to external data is based on adaptors; sources include historians, databases, and KAPPA-Server installations (4).
The platform calculations cover wavelet filters and include a processing service with some predefined tasks (shut-in identification, corrected production, etc.) plus an open extension framework supporting Excel-like functions, or user tasks in C# or Python (5).
Among the most important components are micro-services that provide the DDA services of the KAPPA-Workstation modules (6). Through them, automated workflows can manipulate KAPPA-Workstation documents, and trigger actions such as loading data, running models, regressions, etc.
User interaction with the platform is through a web browser and possible from any type of device (PC, tablet, mobile (7) The UI is 'responsive' i.e. it will adapt to the particular device it is launched from.
Finally, exchanges with KAPPA-Workstation are possible with drag-and-drop, and active data links from documents to K-A data streams (8).