Shut-in Classification
Introduction
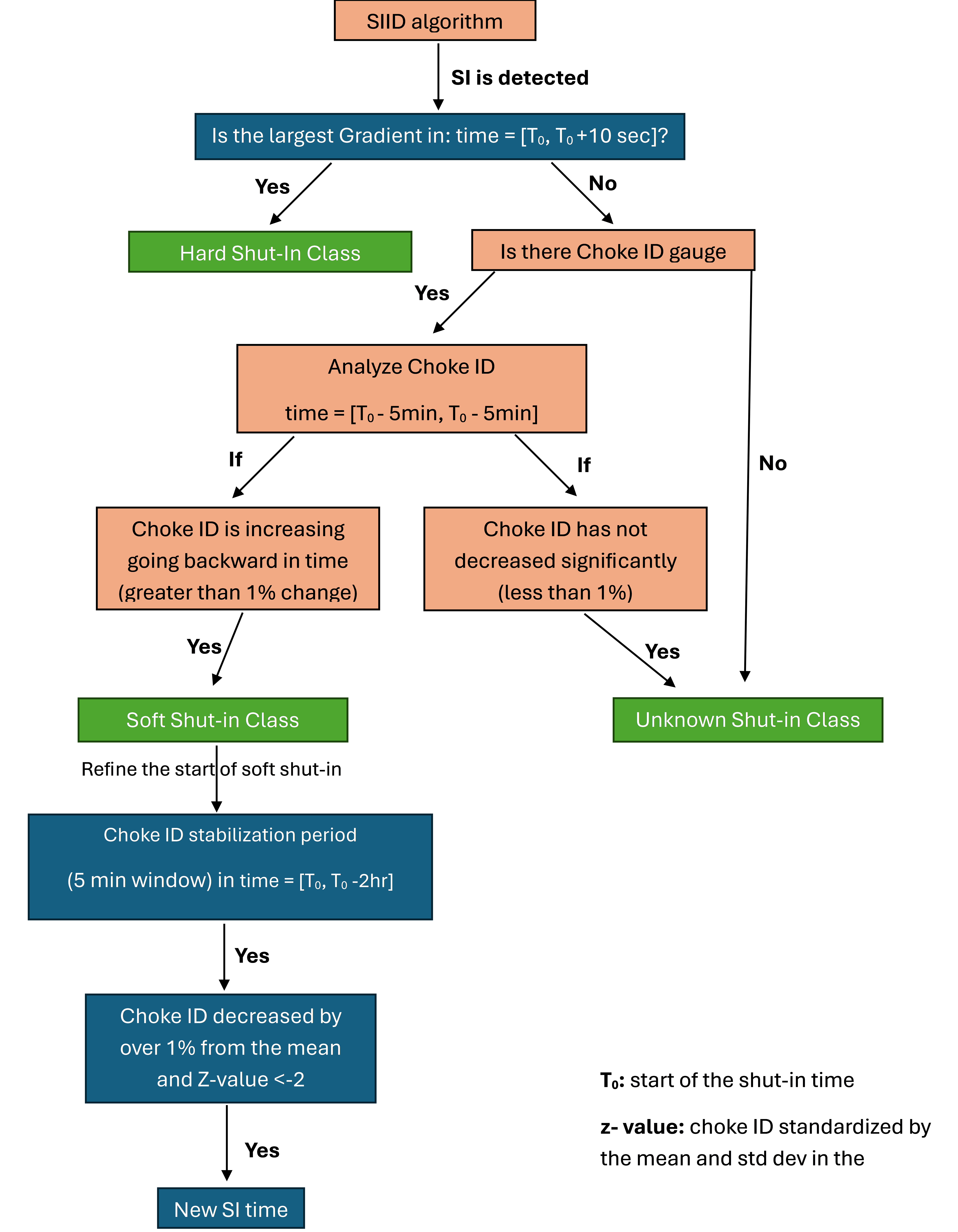
When using the built-in shut-in identification user task, it can add classification attributes to the detected shut-ins using the choke ID gauge, if available. Below is a detailed description of the workflow.
Description
Important
Timestamp1 = Start of the shut-in time as detected by the SI algorithm.
Timestamp2 = Largest measured pressure gradient.
The classification is made using the following logic:
Hard Shut-In:
A shut-in is classified as Hard if the largest measured pressure gradient (Timestamp2) occurs within 10 seconds of the shut-in start time (Timestamp1) as detected by the SI algorithm. The choke ID does not affect this classification.
Soft or Unknown Shut-In:
If the largest pressure gradient is not within 10 seconds, the choke ID is used to classify the shut-in as either Soft or Unknown.
A 5-minute window (both forward and backward) from the SI time is analyzed to determine changes in the choke ID.
If the choke ID decreases insignificantly (less than 1%) or if no choke data is available within this window, the SI type is marked as Unknown.
If the choke ID increases (more than 1% change) when moving backward in time, the SI type is marked as Soft.
Refining the Start of Soft Shut-Ins:
For all Soft shut-ins, the start time is refined by analyzing choke ID values in 5-minute increments going backward, up to 2 hours before the detected start time, to identify a stabilized period.
A stabilized period is defined as a time when the choke ID shows less than a 1% change in its mean value.
Once a stabilized period is identified, the choke ID is analyzed point-by-point moving forward to determine where the choke ID decreases significantly.
Determining the New SI Time:
A new shut-in time is established when:
The choke ID decreases by more than 1% compared to the mean value in the previous 5-minute window
The z-value (standardized choke ID relative to the mean and standard deviation of the stabilized period) is less than -2.
Note
The -2 z-value indicates that the choke ID is two standard deviations below the mean of the choke ID values in the previous 5-minute window.