KAPPA-Automate Concepts and Elements
KAPPA-Automate (K-A) is built upon certain key elements, which constitute the overall system architecture. The topics below explain these elements in details, along with any associated concepts on how K-A handles certain things.
The Wellbore object describes the physical structure and configuration of a wellbore. It includes detailed information such as the well trajectory, casing and tubing strings, gas lift valves, and perforation zones.
In dynamic well environments, where the wellbore configuration may change due to interventions such as completions, tubing installations, or workovers, the Wellbore object supports time-dependent configurations with associated timestamps. This enables accurate tracking of historical wellbore states and modelling of well conditions over time.
The wellbore object is an essential input for calculating bottomhole pressure (BHP), and generating inflow profiles.
To define a wellbore object, the following inputs are required:
Trajectory
Defines the spatial path of the wellbore. Must be provided as directional survey data. Each survey point must include: measured depth (MD), true vertical depth (TVD) and inclination.
Geometry
Specifies the physical configuration of the wellbore along the depth. Each segment must define its structural state. Open hole, cased hole, or includes installed tubing.
For cased or completed intervals, define each string dimensions: Inner Diameter, Length, Thickness and Roughness.
Flow Path
Describes the production flow path in the wellbore. This is essential for production modelling and pressure loss calculations.
The flow path must be defined, e.g., though tubing, casing or annulus.
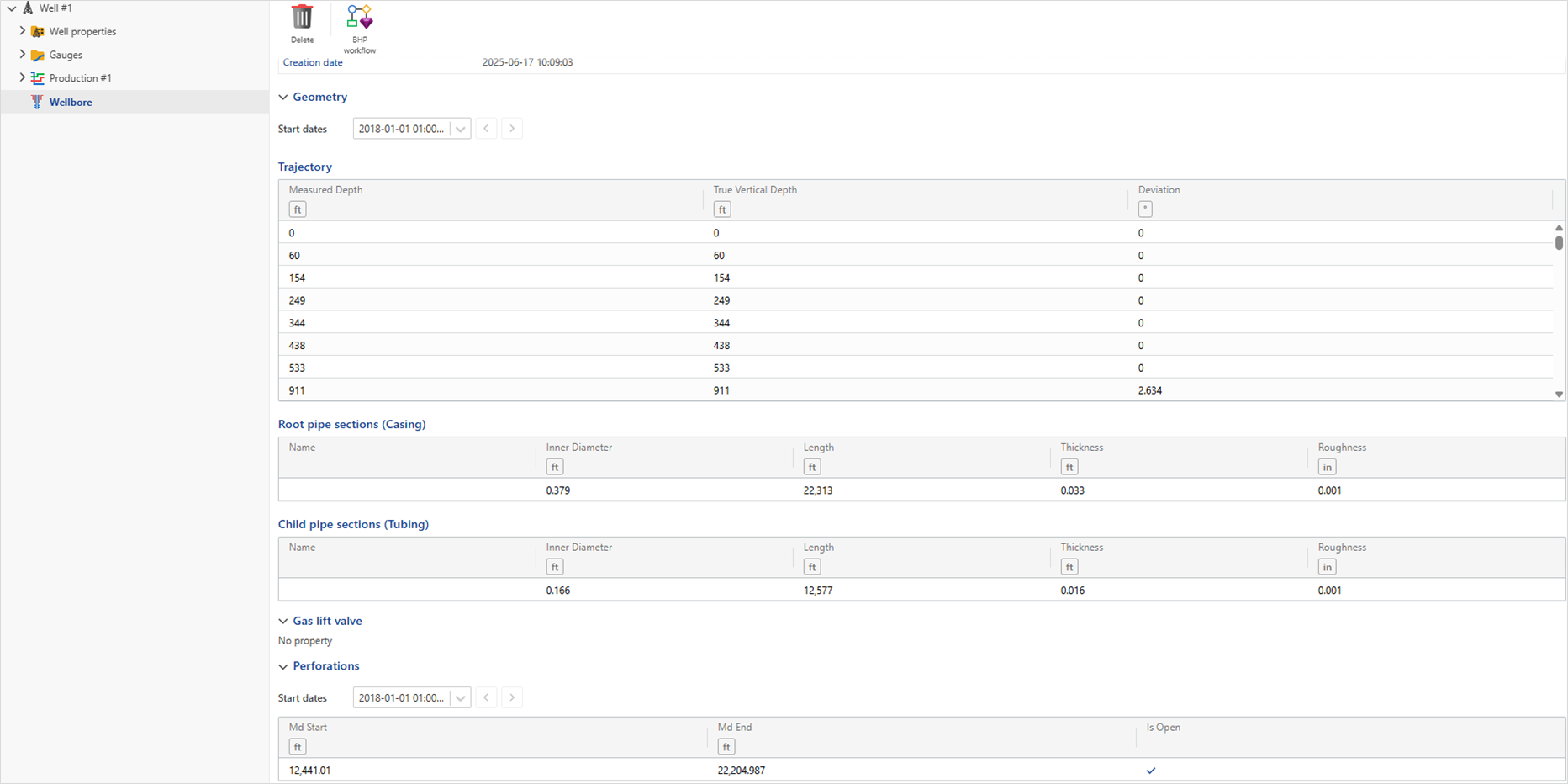
The Wellbore object includes definitions for gas lift valves, which are essential for modeling wells that use gas lift for production. It also allows the specification of perforation zones, which are used to generate inflow profiles.
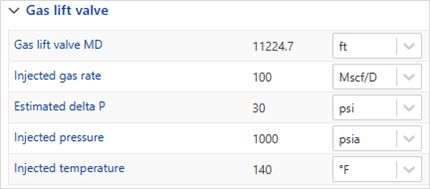
Gas lift valve
For gas lift wells, the details of the gas lift valves can be specified:
Gas lift valve MD: This parameter specifies the installation depth of the valve and is mandatory when a Gas lift valve is defined.
Injected gas rate: This is an optional parameter in the BHP workflow, as the injected gas rate is predefined in the Gas Lift section.
Estimated delta P: optional field.
Injected pressure: optional field.
Injected temperature: optional field.
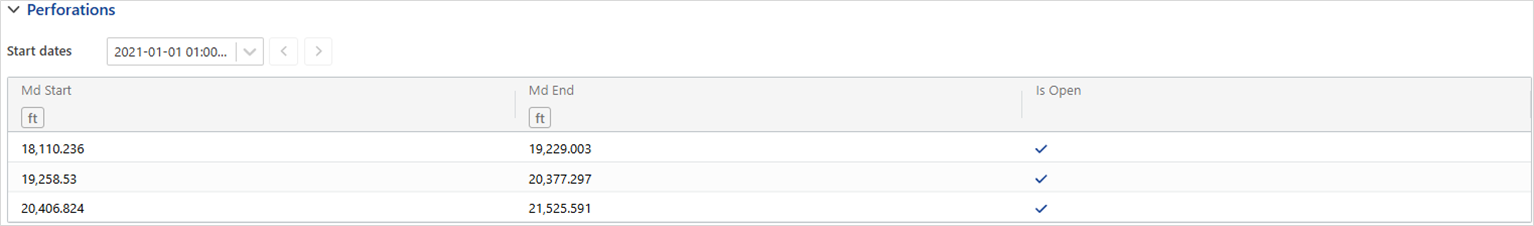
Perforations
To define perforations, the following information must be provided for each perforation interval:
MD Start: Measured depth at the start of perforation interval.
MD End: Measured Depth at the end of perforation interval.
Is Open: Perforation status, open or closed (default is open).
Procedure to create a Wellbore object
Wellbore objects can be created via the multi-well load process. This requires that wellbore data be stored in a database structured according to the KAPPA SQL schema.
Prerequisites
Wellbore data must be populated and available within the KAPPA SQL schema. It is strongly recommended to populate all available data fields, including non-mandatory ones. If certain fields are missing, default values will be assigned during the wellbore object creation.
The mirroring data source and the multi-well load data source must be correctly configured and validated.
Procedure
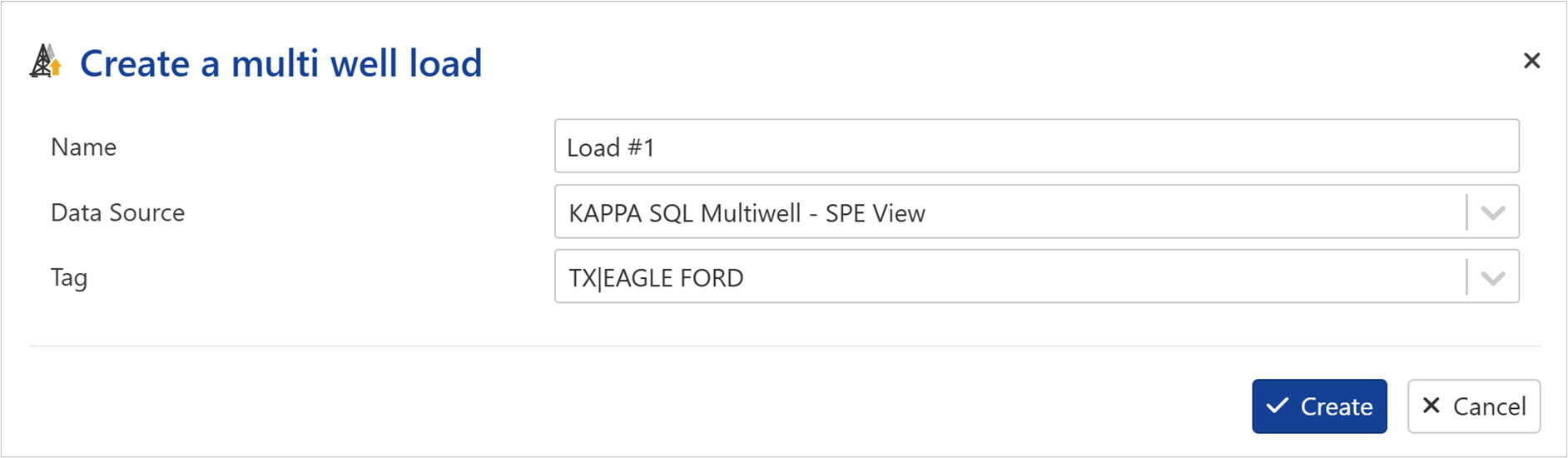
Provide a Name for multi well load.
Select the Data Source.
Select the Tag (filters configured in the multi-well load setup).
Click Create.
Once the multi-well load process is completed the wellbore object is displayed under well node.
Alternative method: Using KAPPA-Automate SDK.
Wellbore object can also be created using KAPPA-Automate SDK.
Prepare the deviation survey and wellbore geometry definition. If available, also include gas lift valve and perforation data.
Supported formats include Excel files and SQL databases, both must follow the KAPPA Automate format.
Run the Python script.
Execute the script to process the input data.
Create the wellbore object.
The script will generate a Wellbore object under the Well node.