Tutorial 2
This tutorial expands the scope to include oil, water, and gas phases. In addition to covering the basic and advanced PDG workflows, you will also explore the use functions and the PTA dashboard.
Create a well
To add a well, select the field and under the Info tab, click on Well ,  , among the options listed at the top:
, among the options listed at the top:
 |
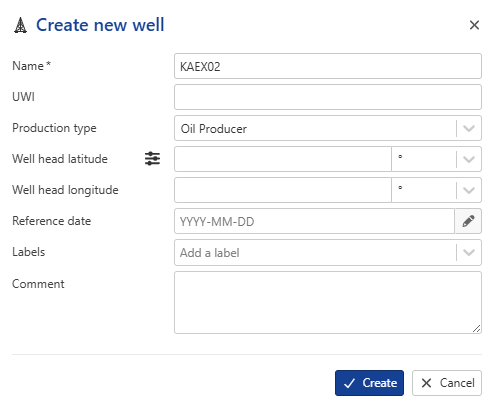
Change the Field Name to KAEX02 , set Production type to Oil Producer, keep all the other information as default.
 |
Click on Create.
The well will be listed in the field hierarchy:
 |
Mirroring and Filtering Gauges
Gauges are used to store time lapse data. Once created, a Gauge automatically mirrors (copies) data from a tag located in a historian. Gauges can store data as points or steps.
Creating a Gauge
To create a gauge, select the well and under the Info tab, click on Gauge among the options listed at the top:
 |
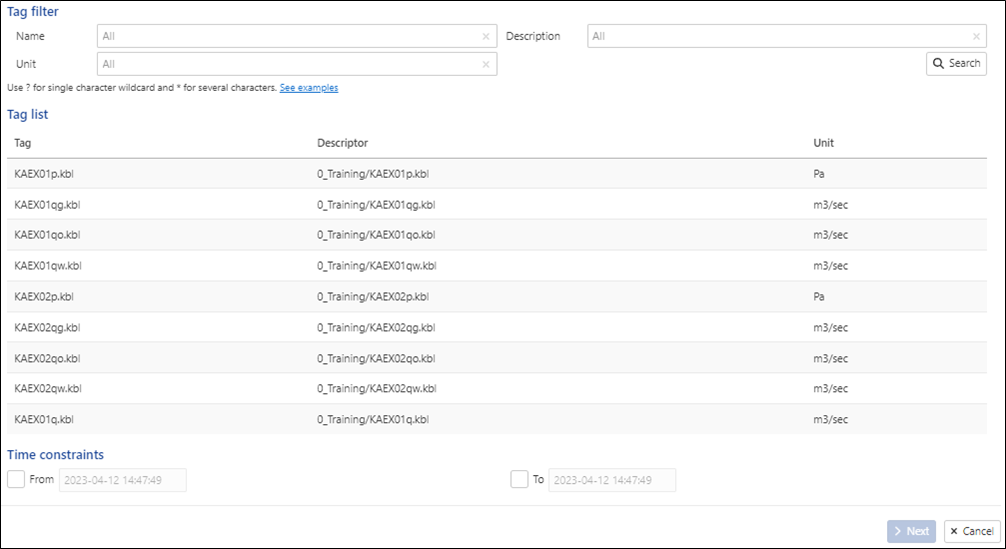
The Load window dialog prompts the user to select the data source. Select the BLI Gauges data source where the training datasets are located. Leaving the tag filters blank, click on  to display a list of all the gauges located in the data source:
to display a list of all the gauges located in the data source:
 |
Data source connectors are predefined links to the company’s data Historian or KAPPA-Server installation and are set up by Administrators of the KAPPA Automate platform.
For this exercise, we will be loading the following gauges:
KAEX02p.kbl
KAEX02qo.kbl
KAEX02qg.kbl
KAEX02qw.kbl
Loading Pressure data
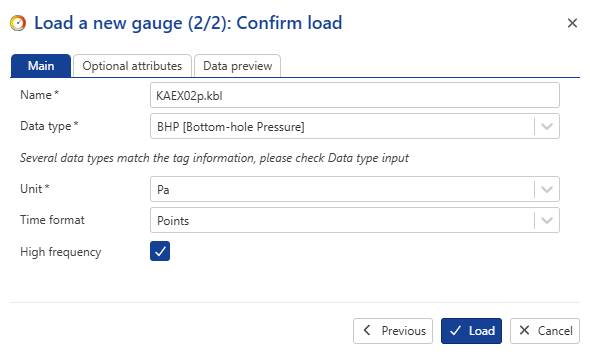
Select KAEX02p.kbl in the Tag list and click on Next.
Change the gauge Name to EX02_BHP, Data type to BHP [Bottom-hole Pressure] :
 |
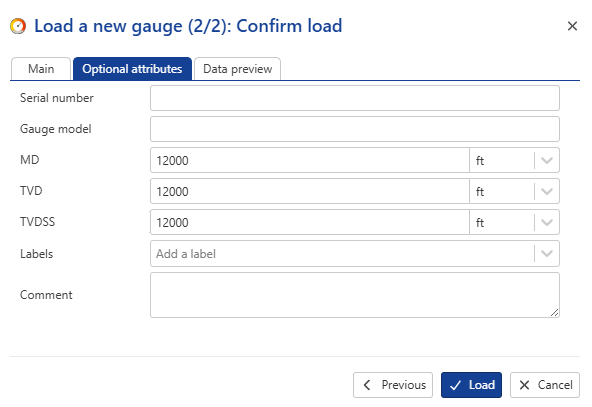
Switch to Secondary parameters dialog and change the MD, TVD and TVDSS to 12000 ft:
 |
Click on Load. The gauge will be listed under a Gauges folder in the field hierarchy:
 |
Filtering High Frequency Gauges
To setup a filtered data, select the gauge and under the Info or Plot tabs, click on Filter among the options listed at the top:
 |
Rename the filtered gauge to EX02_BHP_F:
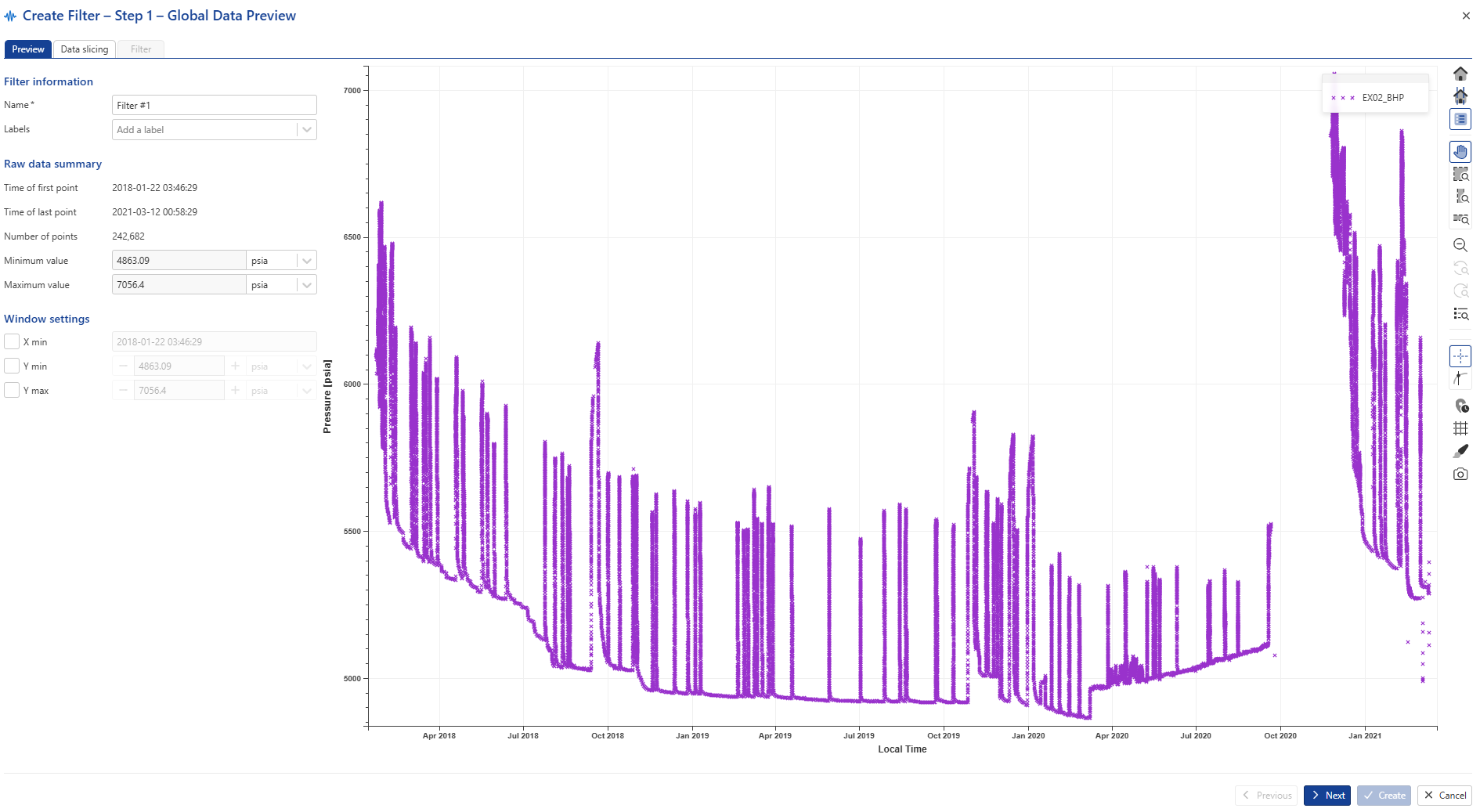 |
Keep the default values and click on Next to navigate to the Data slicing tab:
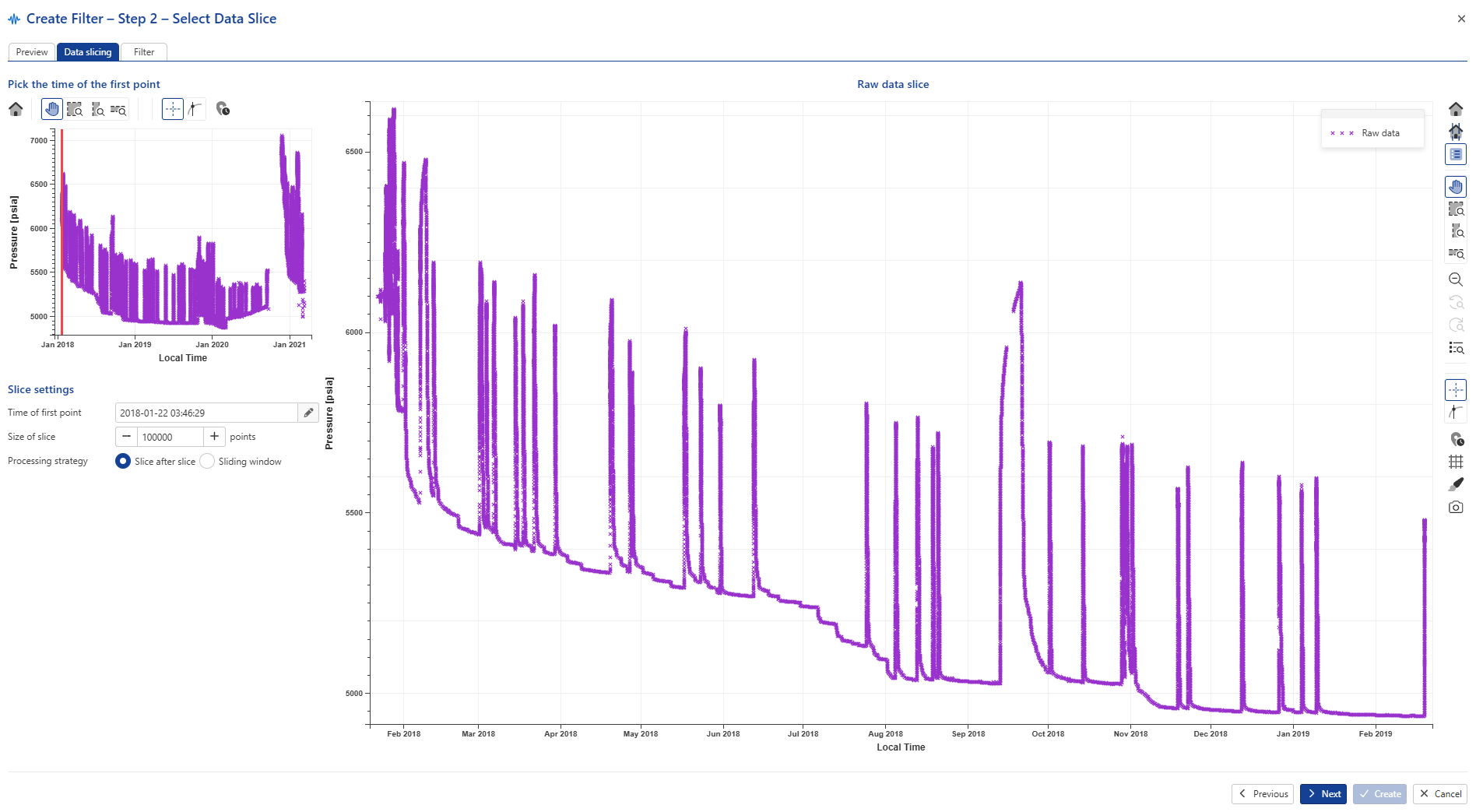 |
Keep all defaults and click on Next.
Enable Output decimated raw data and click on  for the preview:
for the preview:
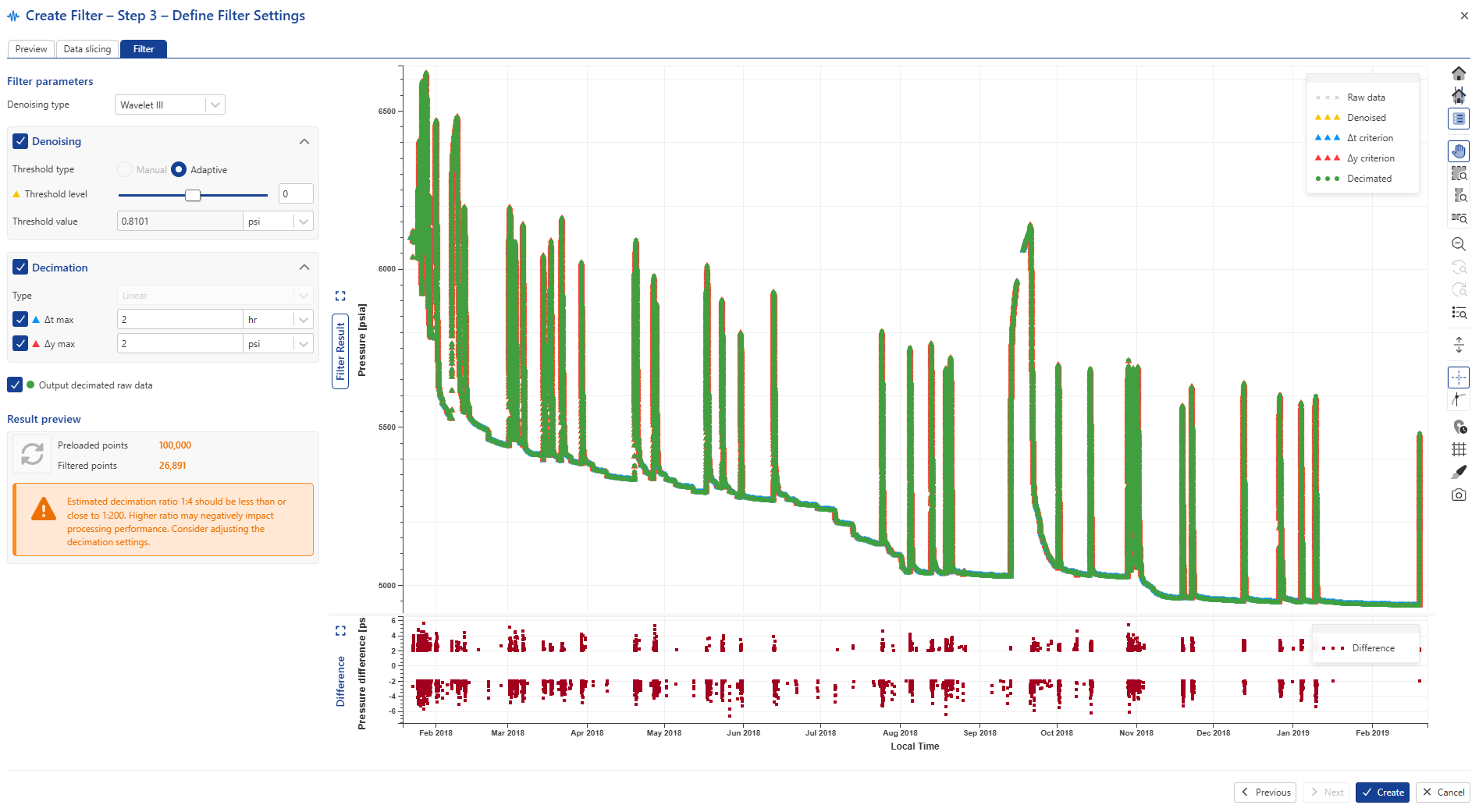 |
Keep the remaining setup as default and click on Create to accept the filter settings.
The filter will be listed under the parent gauge in the field hierarchy:
Loading Rate data
Select the Production #1 node in the field hierarchy and click on Gauge among the options listed at the top.
Repeat the same procedure as for the high frequency pressure gauge and select to load KAEX02qo.kbl in the Tag list.
Change the gauge Name to EX02_qo, Time format to Time at end and input a First step duration of 24 hrs:
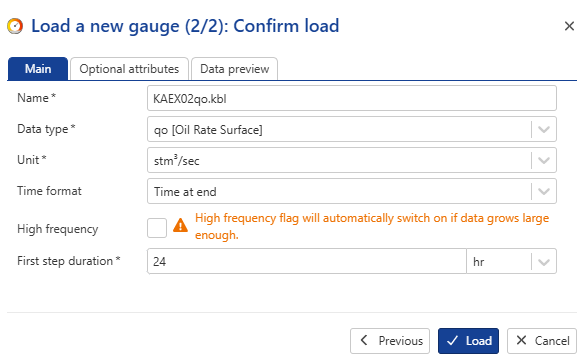 |
Click on Load. The oil node will be filled under the production node:
 |
Repeat the process for KAEX02qg.kbl and KAEX02qw.kbl:
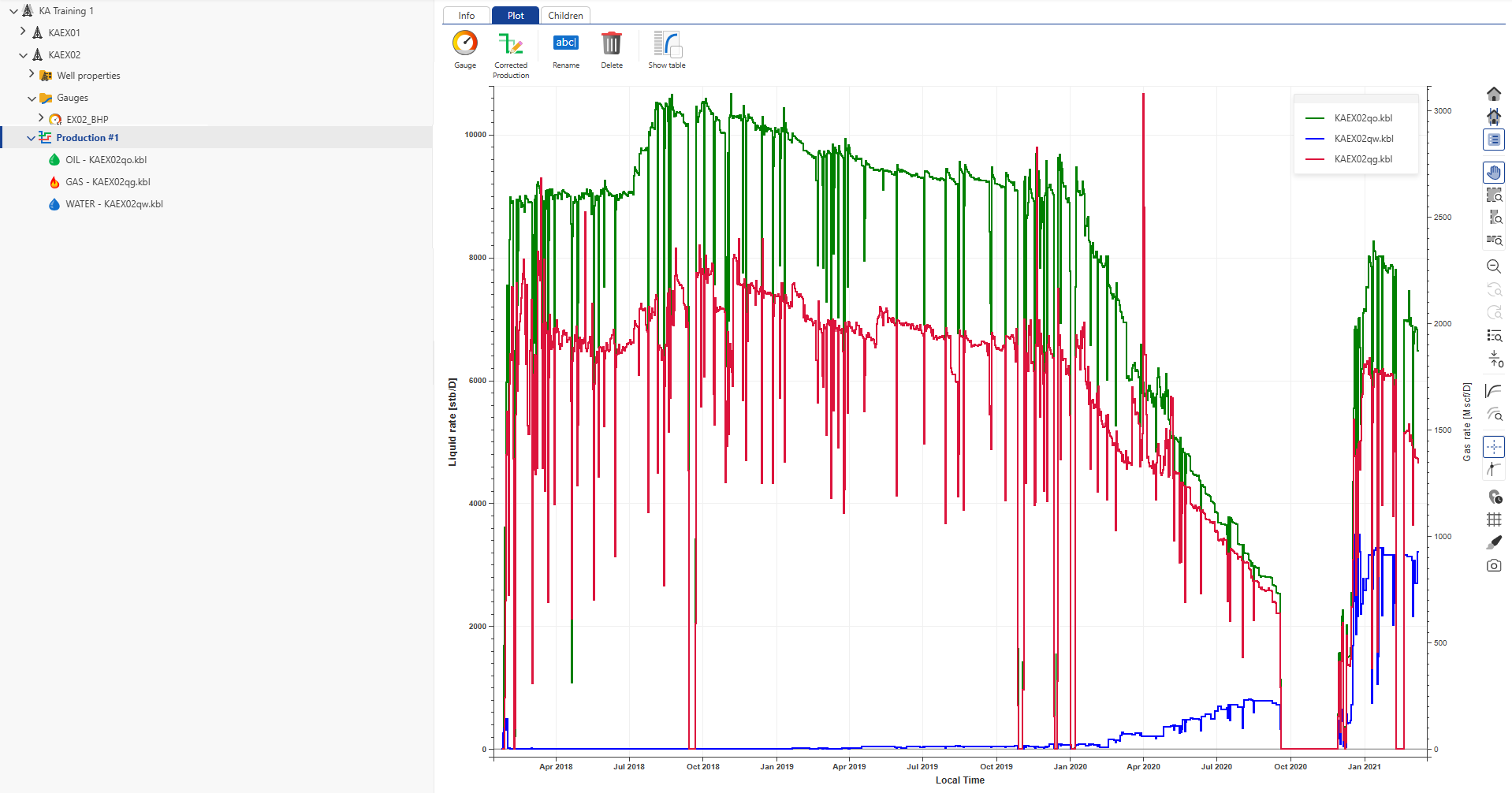 |
Since these rate gauges are low frequency, no filtering is needed.
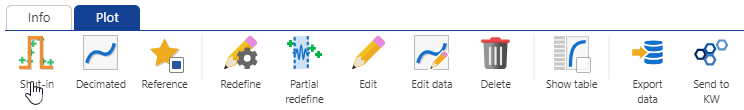
Shut-in Identification
Select EX02_BHP_F in the field hierarchy. Under the Info or Plot tabs, click on Shut-in among the options listed at the top:
In the consequent wizard, set Minimum shut-in duration to 10 hrs and Minimum pressure change to 500 psi:
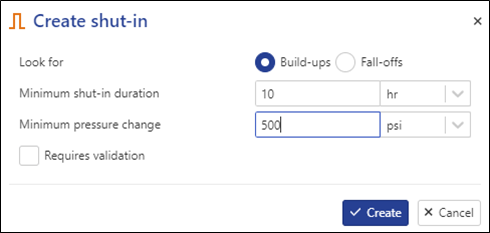 |
Click on Create.
Editing data
Select the gas rate gauge in the field hierarchy and go to the Info tab. Look for the Data summary section:
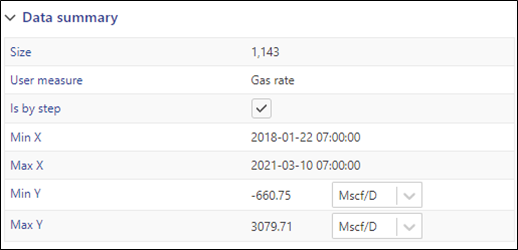 |
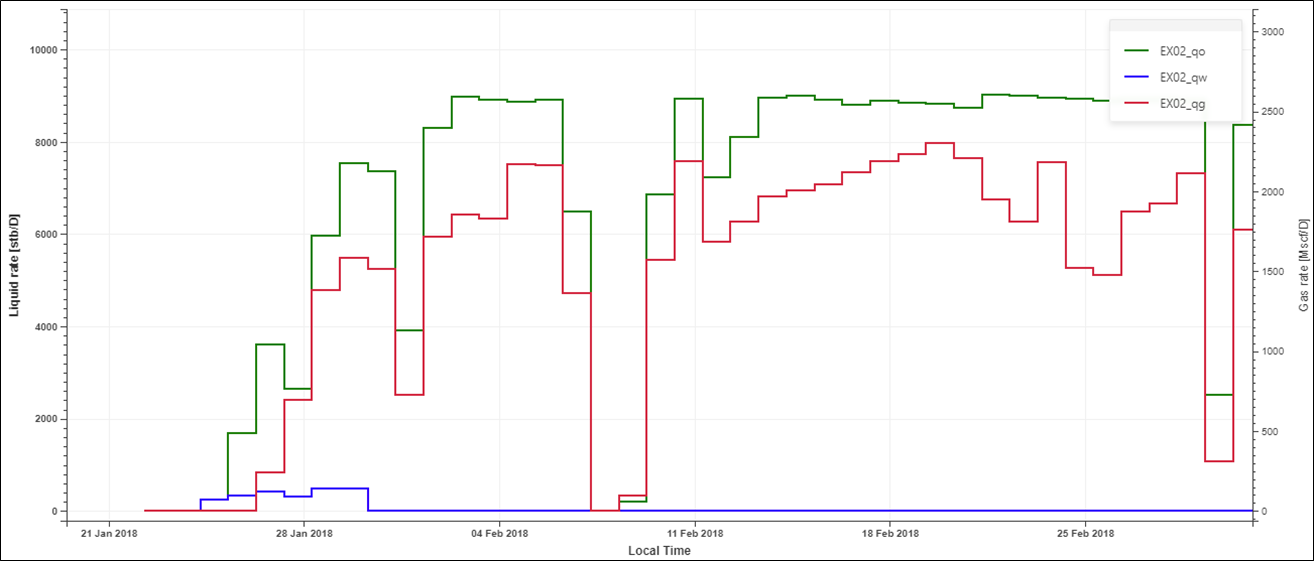
The Min Y field shows there is some negative gas rate data. Switch to the Plot tab and observe that this occurs for only a couple of steps at the beginning of the rate history. The oil and water rates during this period are positive values:
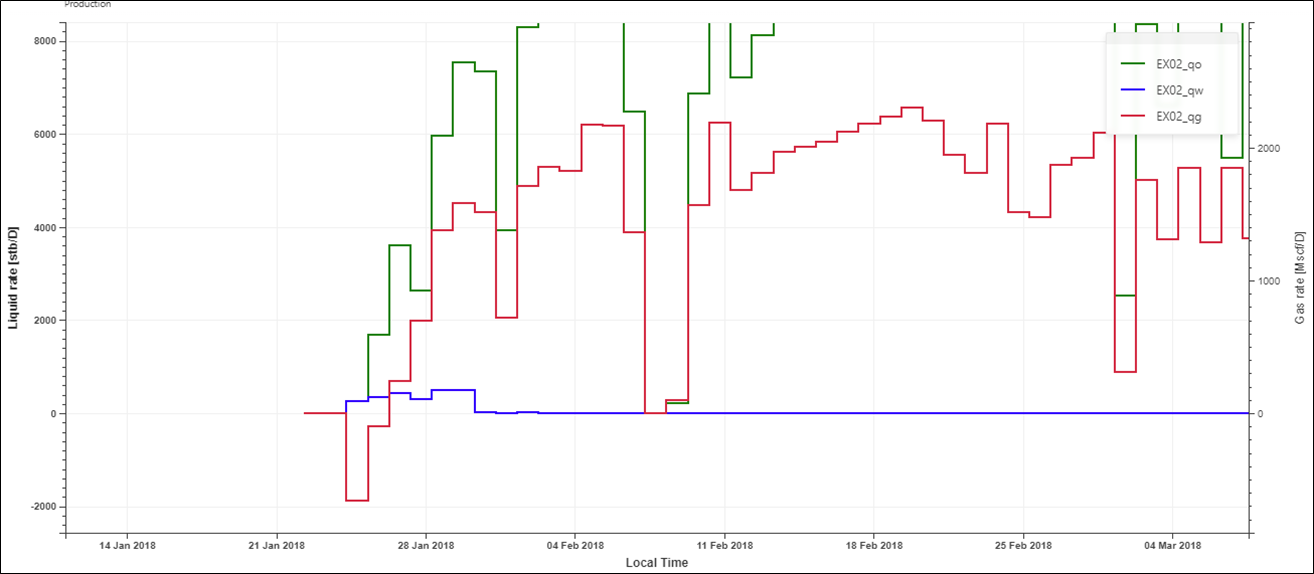 |
This could be an erroneous measurement or due to data storage issues. We will delete these two steps from the gas rate gauge.
Under the Plot tab, click on Edit data,  , at the top:
, at the top:
Zoom in on the negative rates. Select the Step selection,  , option from the ribbon at the top and click on the first negative rate step:
, option from the ribbon at the top and click on the first negative rate step:
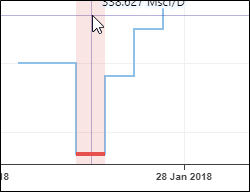
Click on Delete steps,  , in the ribbon at the top. The selected step will be deleted and the Edit data mode will exit. Enable Edit data again, select the second step and delete it as before.
, in the ribbon at the top. The selected step will be deleted and the Edit data mode will exit. Enable Edit data again, select the second step and delete it as before.
 |
Corrected Production
Once shut-ins have been identified, the logical Shut-in channel can be used to create a corrected production channel.
Click on the Production #1 node and under the Info or Plot tab, click on Corrected Production:
 |
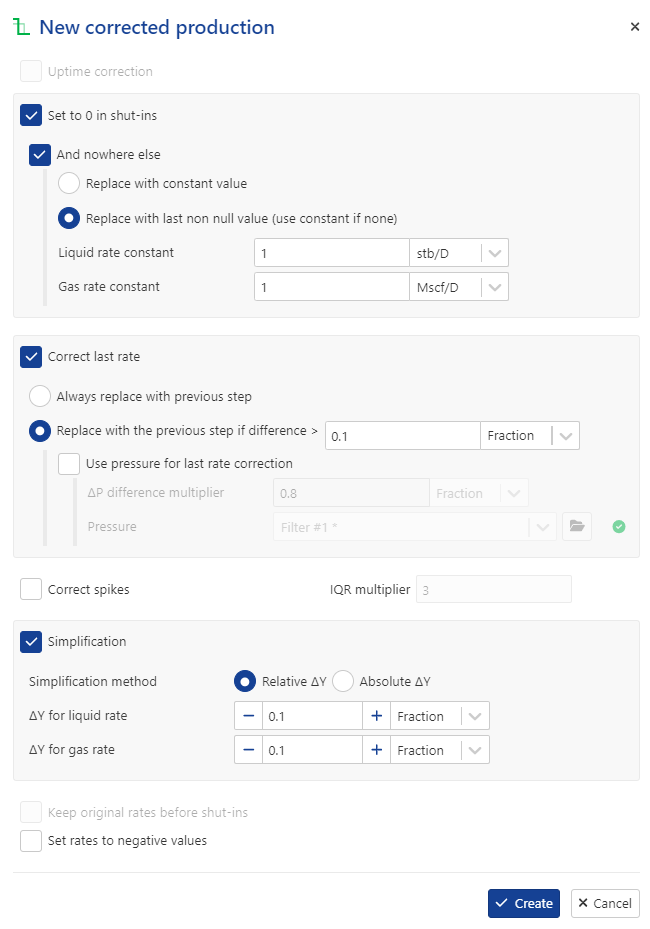
Set the following parameters:
Uptime correction: disabled
And nowhere else: enabled
Correct last rate: enabled
Select Replace with the previous step if difference and keep the default value
Simplification: enabled
ΔY for liquid and gas rates = 0.1
Viewing PTA Loglog Plot inside KA
Once the corrected production has been created, click on the Shut-in node in the field hierarchy and under the Plot tab, click on View loglog ,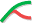 , among the options at the top. Switch the Pressures gauge to (raw) EX02_BHP_F gauge, click on
, among the options at the top. Switch the Pressures gauge to (raw) EX02_BHP_F gauge, click on  and display all Shut-ins:
and display all Shut-ins:
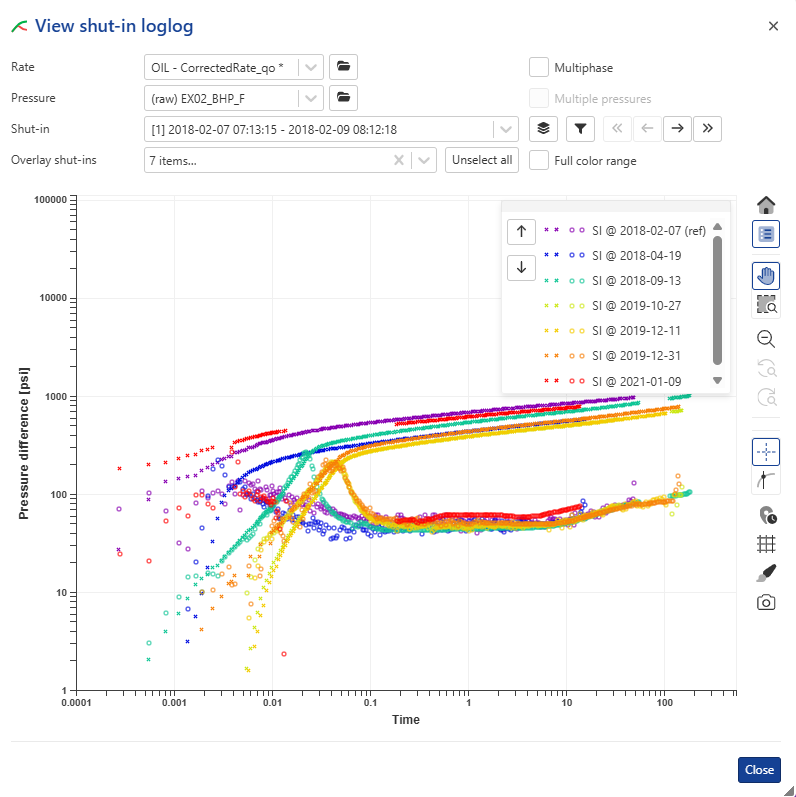 |
Note
In the background, KAPPA-Automate is calling the PTA µ-service, which creates a temporary Saphir document, extracts the shut-in and sends the loglog plot data back to KA to plot. µ-services will be discussed later during the training.
Creating User Plots
We will now create a few custom plots to better view what has been done so far.
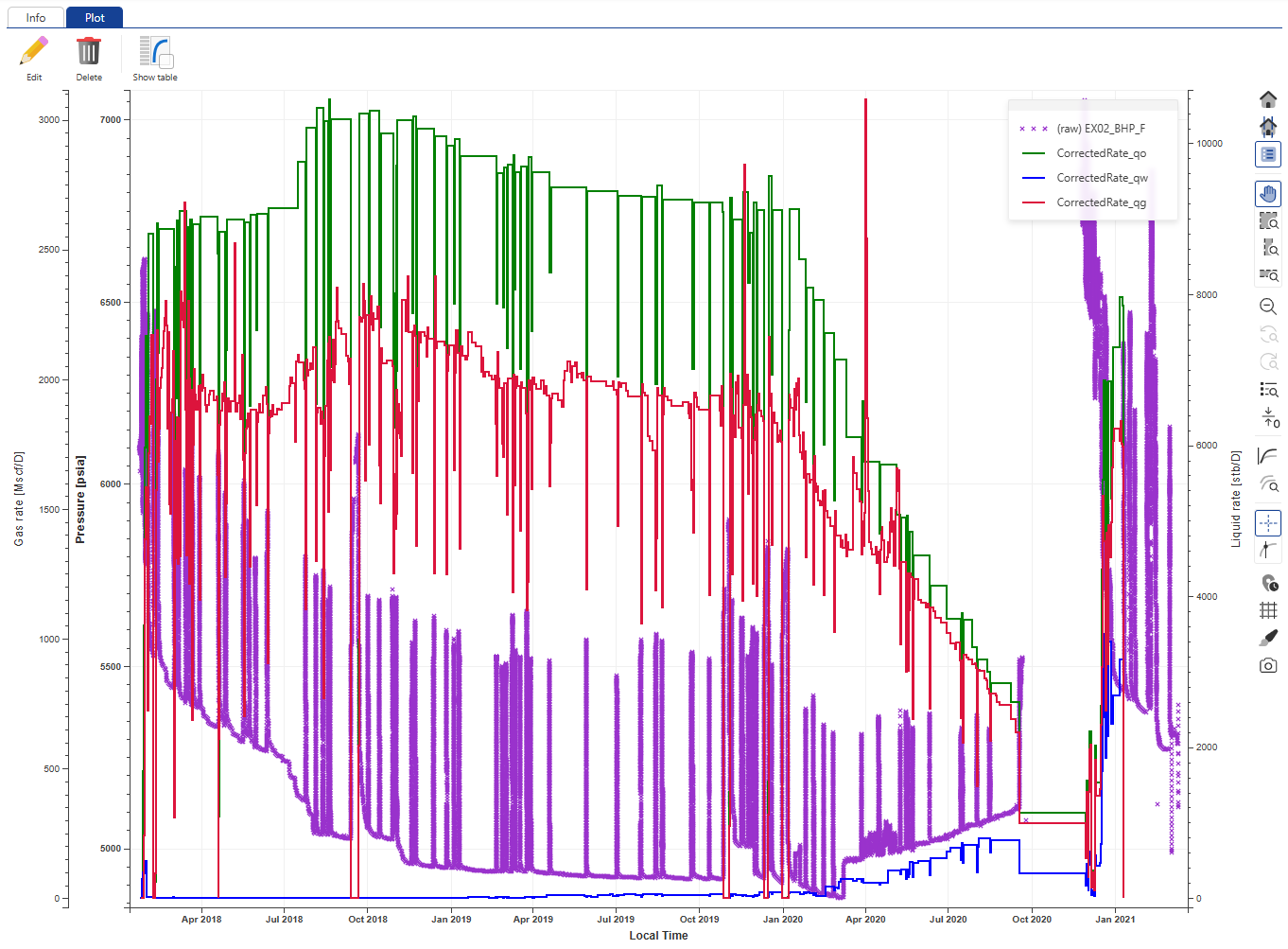
Select the well in the field hierarchy and under the Info tab, click on Plot,  , among the options at the top. Call the Plot Production Data and select (raw) EX02_BHP_F gauge and the corrected production nodes:
, among the options at the top. Call the Plot Production Data and select (raw) EX02_BHP_F gauge and the corrected production nodes:
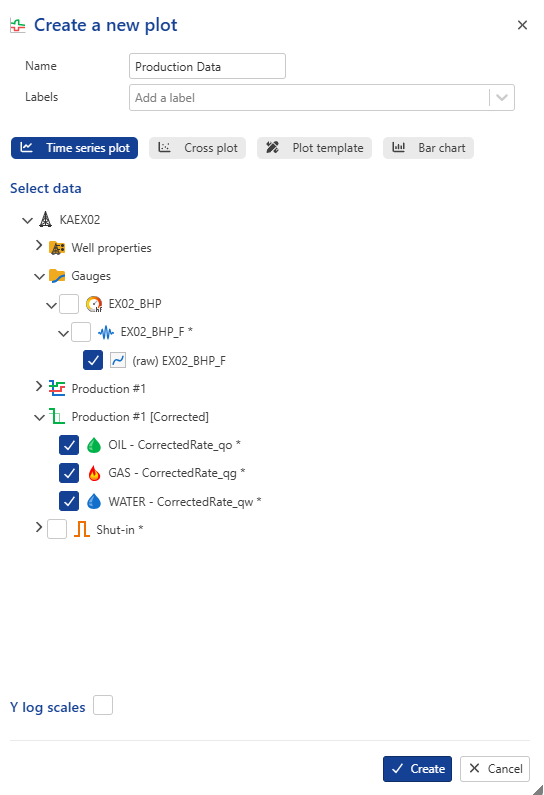 |
Click on Create.
The plot shows that the rate data are synchronized with the pressure data. To inspect in detail, use the zoom in functions.
 |
Opening a KA field in KW Browser
Select the field node in the KA hierarchy and under the Info tab, click on Open in KW,  , in the options at the top:
, in the options at the top:
 |
This will launch KAPPA-Workstation 5.50.xx with the KW Browser open. The field will be listed in the browser:
 |
Gauges of interest shall be sent to Saphir through a Drag ‘n’ Drop (DnD) via the KW Browser. For this, the target Saphir (or Topaze, Rubis etc.) file must first be created/opened in KW.
PTA Document
Create a multiphase Saphir file (Oil, Water and gas) using default parametrs.
Save it under the name EX02_iPTA_Blank file.
Transfer gauges to KW
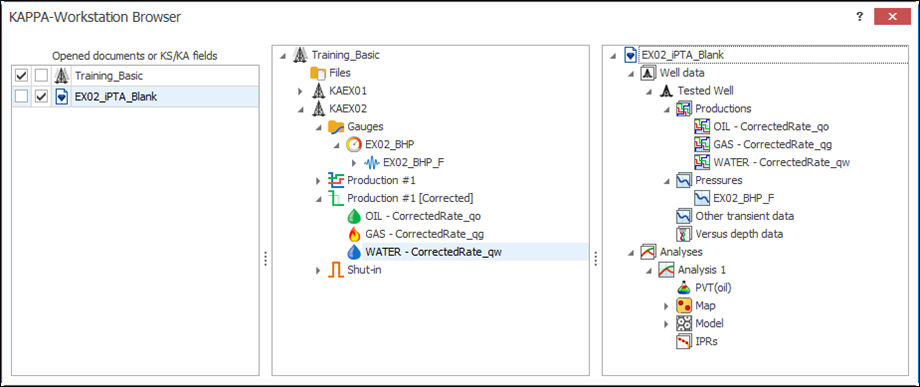
In KW Browser, select the KA field on one side and the Saphir document on the other. Expand the field hierarchy to the BHP_LF and corrected production channels. Expand the Saphir document to well data.
Drag and drop EX02_BHP_F to the Pressures node and the three corrected production phases to the Productions node in Saphir:
 |
Go to Edit Q and delete all the rate data after the Build-up #1. This is to replicate a realistic scenario where we have a BU in the early life of the well as our starting point for iPTA. Go to Edit P and repeat the same for pressures.
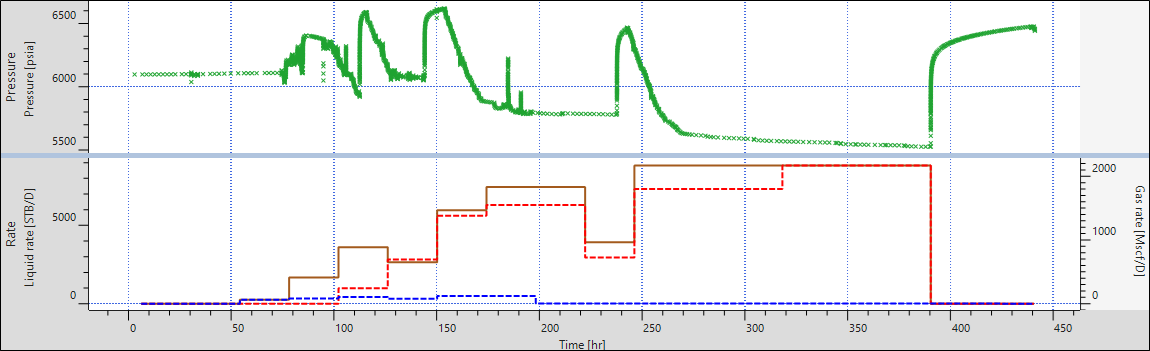 |
Extraction + Model in KW
Extract the BU data using total rate. Set boundary analysis tools to single fault. Match the tools to data on the loglog plot:
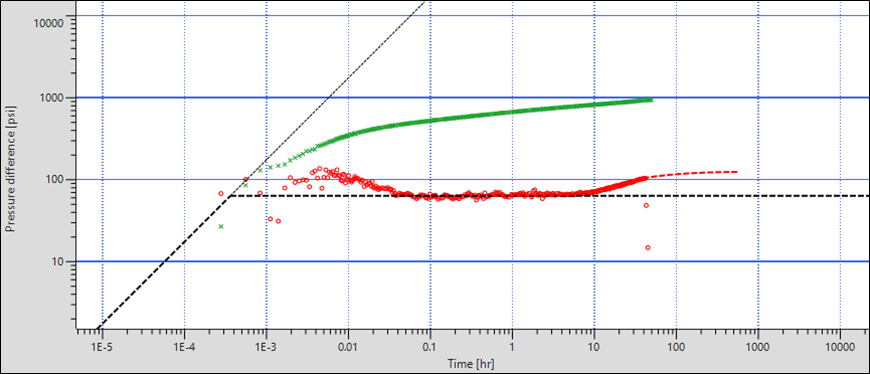 |
Generate auto-analytical model (Shift + Analytical), followed by Improve to obtain a decent match: Save the file.
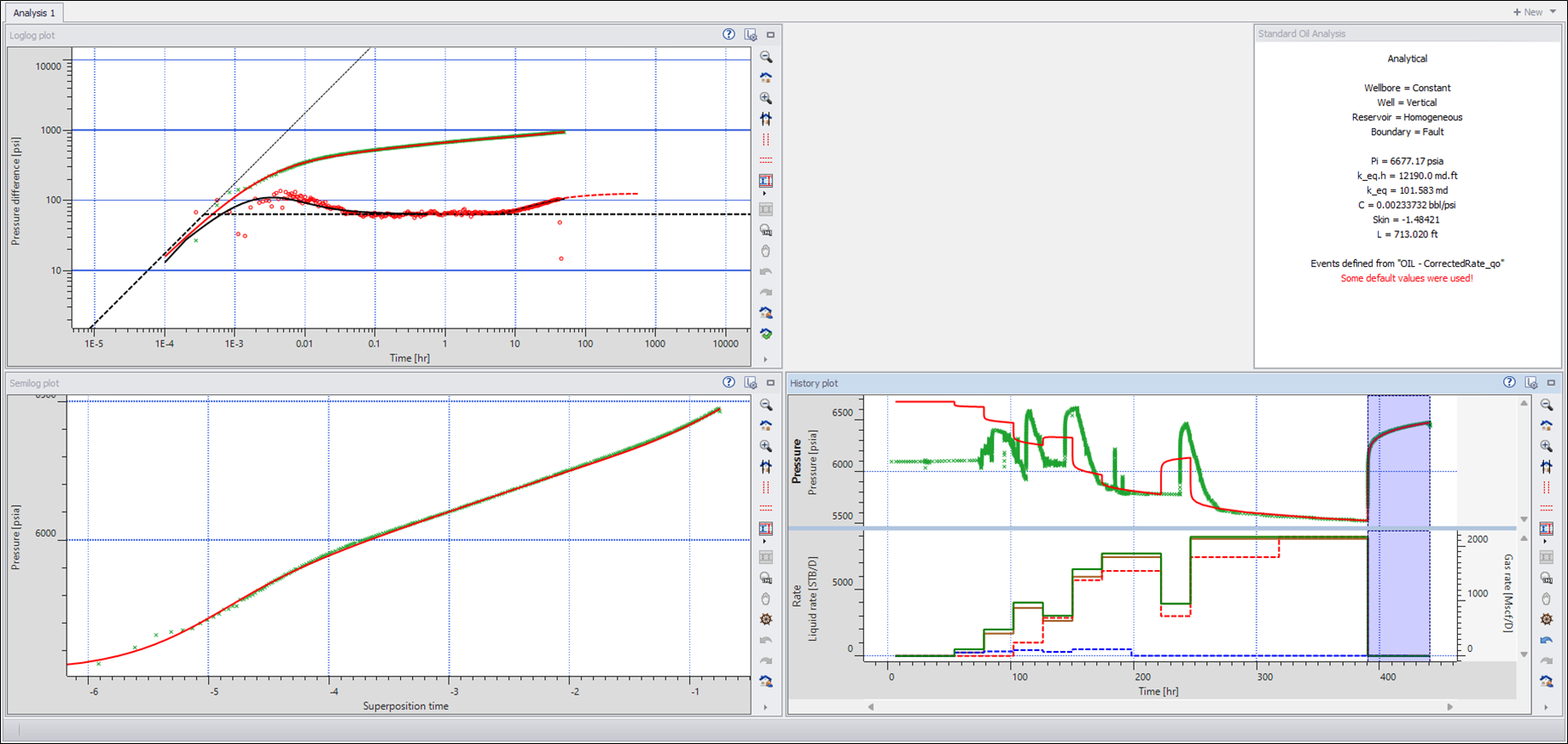 |
Call it EX02_iPTA_Start.
Upload KW file to KA
Select the KAEX02 well in the field hierarchy and click on File,  , under the Info tab:
, under the Info tab:
 |
Select the files and click on Open. A new Files folder will be created under the well where the files will be stored:
 |
Additional files may be loaded using the steps described above. Alternatively, click on the Files folder and use the File option under the Info tab.
It is possible to view in the K-A client the document information and results as well as the main plots.
Content Visualization
When Saphir or Topaze documents are uploaded under a well or field they are automatically pre-processed by KAPPA-Automate. The following are extracted as part of document pre-processing:
Analyses results: To view analyses results, click on the file in the document hierarchy, go to the Info tab and scroll down to the table under the KAPPA results section.
Analysis plots: To view analyses plots, click on the file in the document hierarchy and go to the Plot tab. Users can toggle through the different analyses in the file as well as the plots in each. The following plots are available to view:
Saphir: Loglog plot, History plot and Semilog plot
Topaze: Loglog plot and History plot
Select the EX02_iPTA_Start.ks5 file in the field hierarchy. By Default, the loglog plot from the Saphir file will be shown:
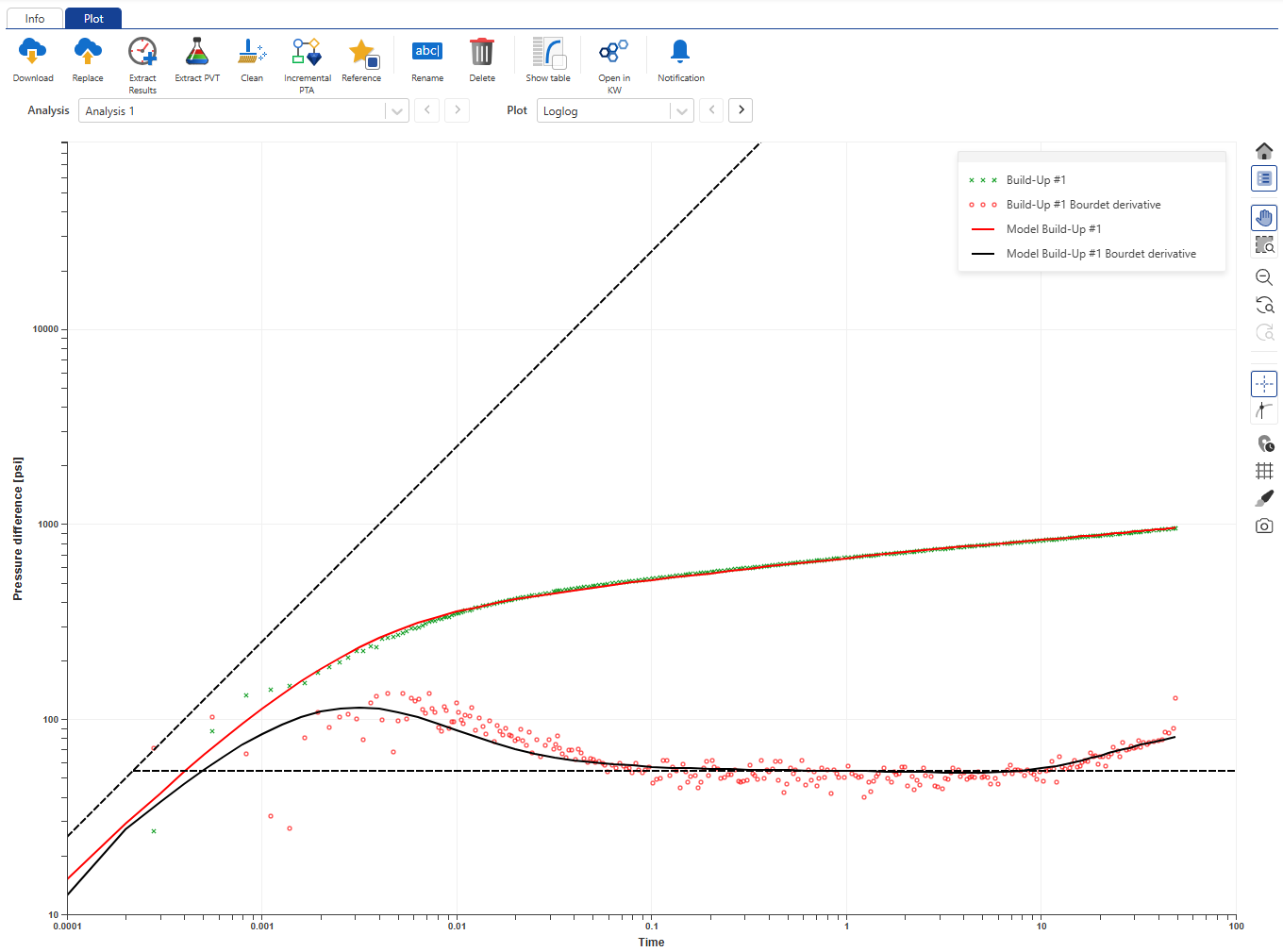 |
Using the Plot dropdown menu, select History plot:
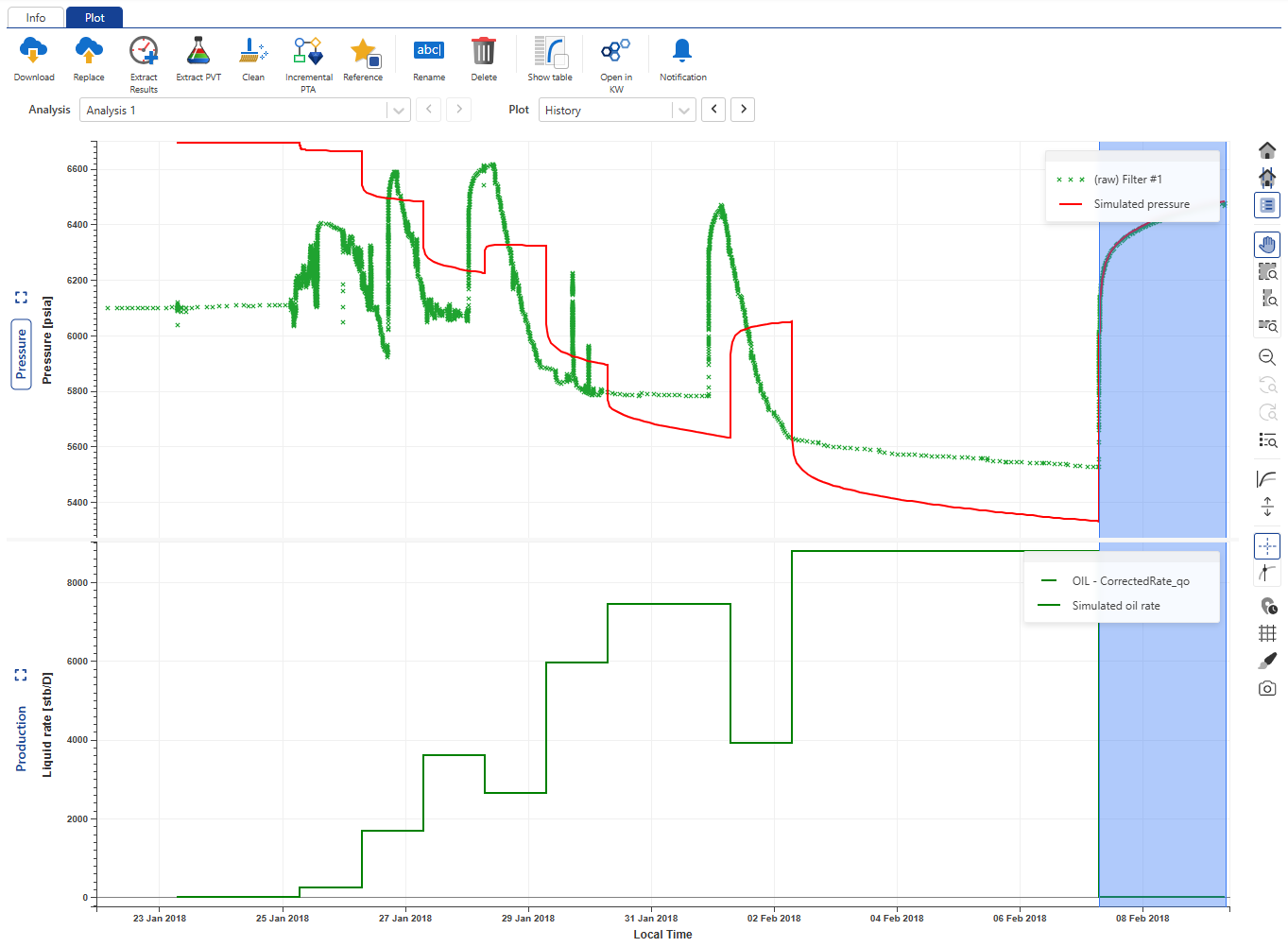 |
Switch to the Info tab and scroll down to view the analysis results:
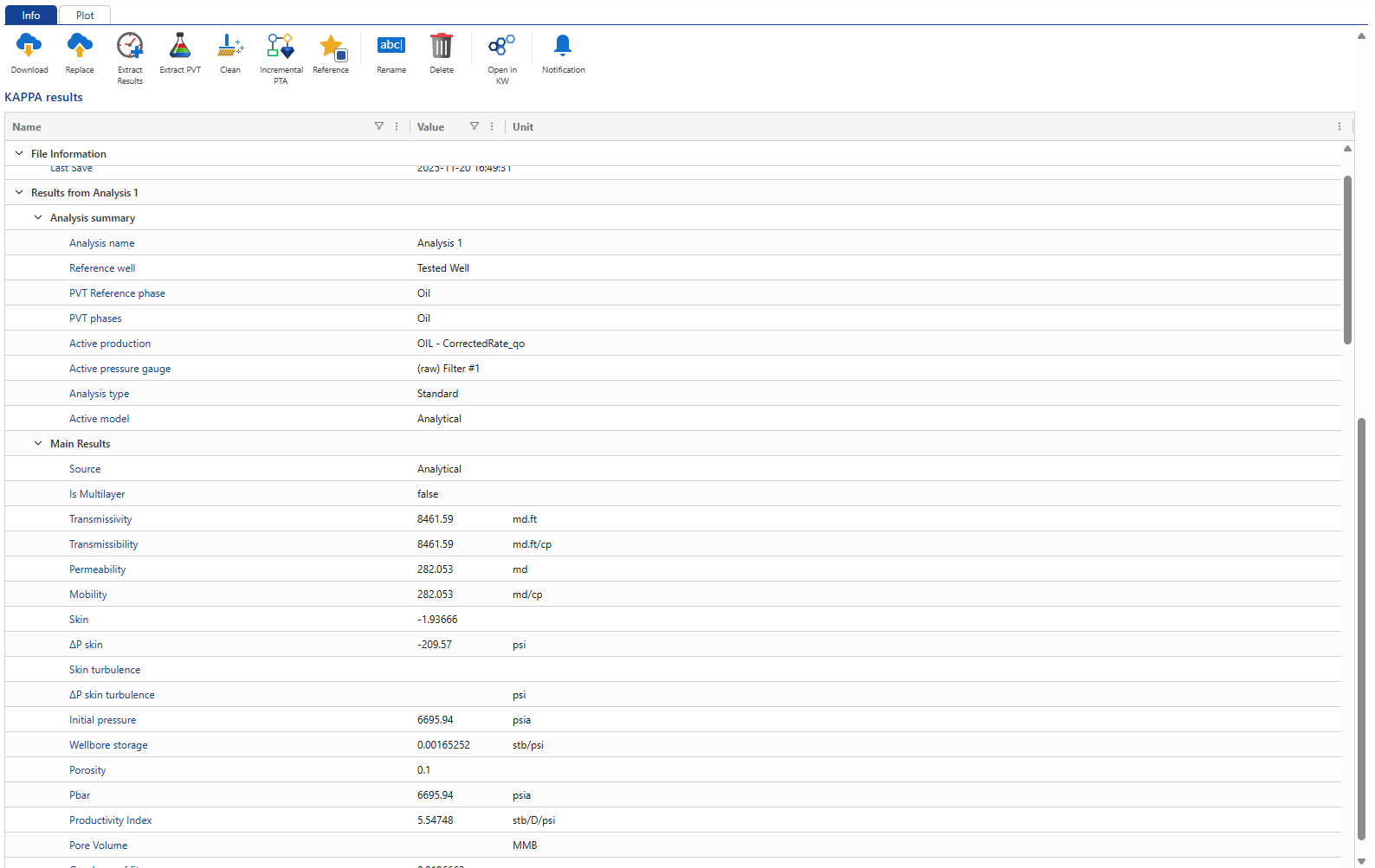 |
Result extraction into well properties
Analysis results can be extracted from the documents stored under a well and saved as well properties, the main use case being to track the evolution of parameters with time. Well properties results can be plotted or used in further processes or computations. Extraction of results can be configured as desired from the XML file contained in the K-W archives. It can be triggered on an individual document, or a folder. Finally, one can extract results from valid analyses only or all of them. Some workflows that create K-W documents automatically also trigger results extraction – this is the case with iPTA or iRTA described next.
Click on Extract Results,  , among the options at the top:
, among the options at the top:
 |
Select Analysis 1 and click on OK. This will populate the File_Name container under well properties:
 |
Inside the File_Name container, click on Permeability and switch to the Plot tab:
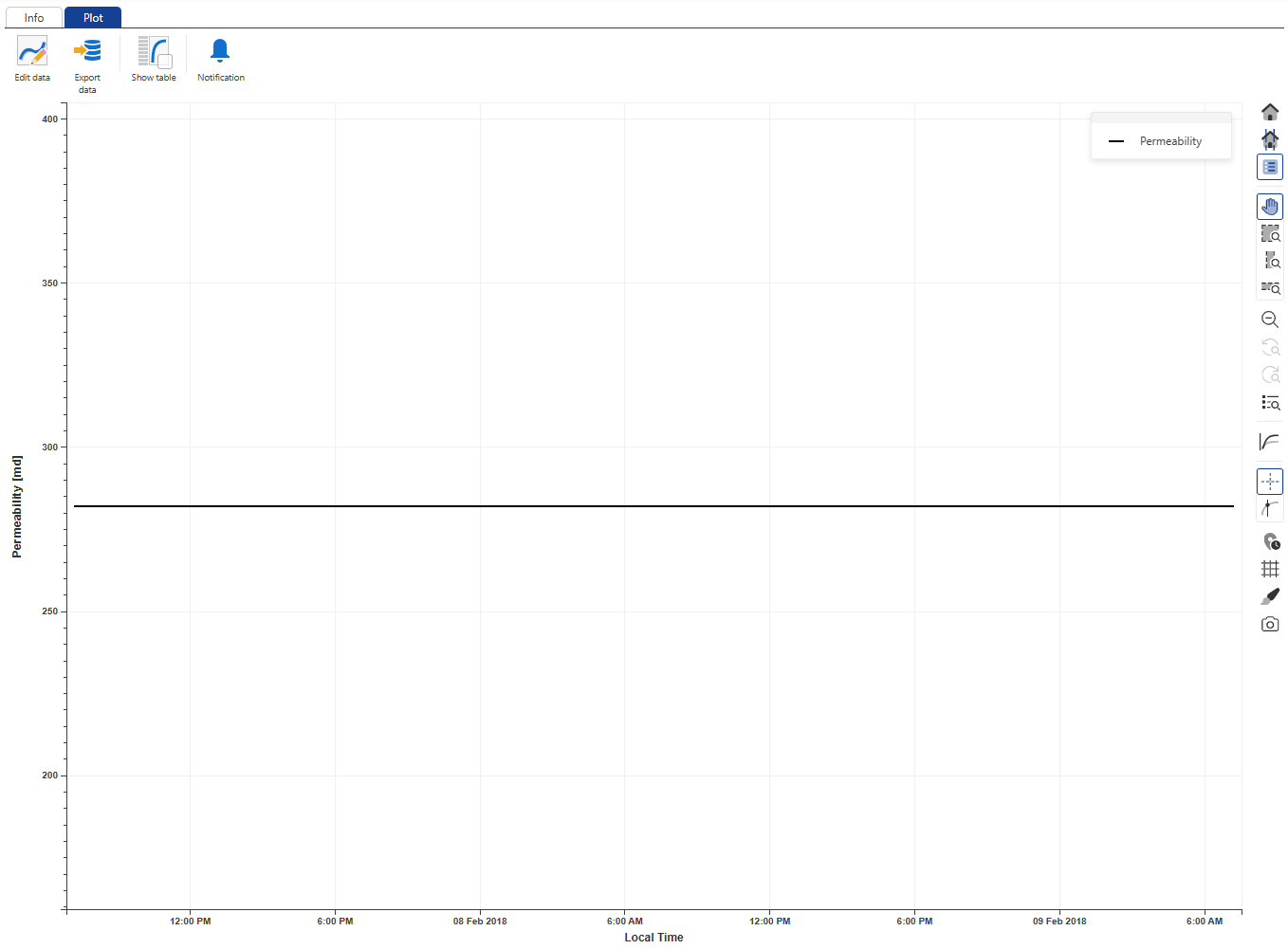 |
Since this is the first extraction for this well, only a single value from the analysis is displayed. View other well properties in the same manner.
Prerequisites
To start an iPTA workflow, the following pre-requisites must be met:
A Saphir file must be uploaded under the well. This file will serve as the seed document for iPTA.
A Shut-in channel mut exist for the well.
A corrected production must exist for the well.
Launching iPTA
To launch iPTA workflow, select a Saphir file (EX02_iPTA_Start.ks5) in the field hierarchy and click on Incremental PTA,  , under the Info or Plot tab:
, under the Info or Plot tab:
 |
This will launch the following iPTA wizard:
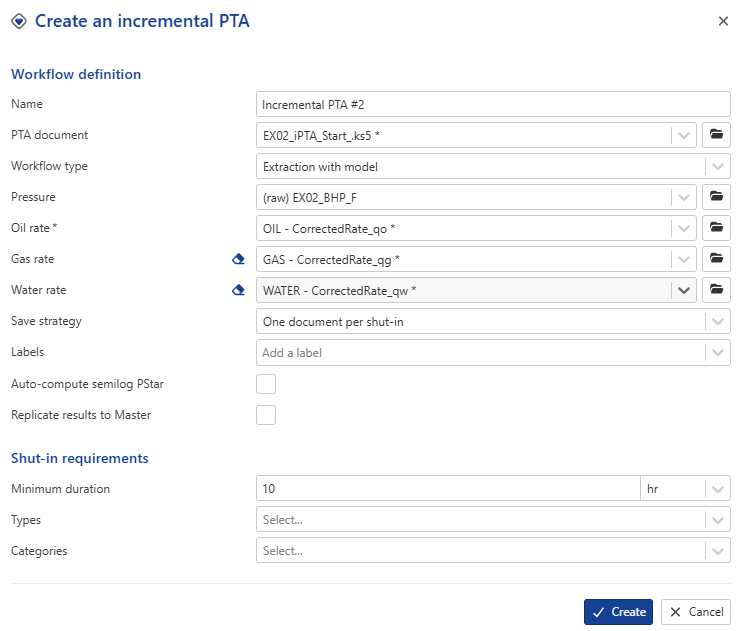 |
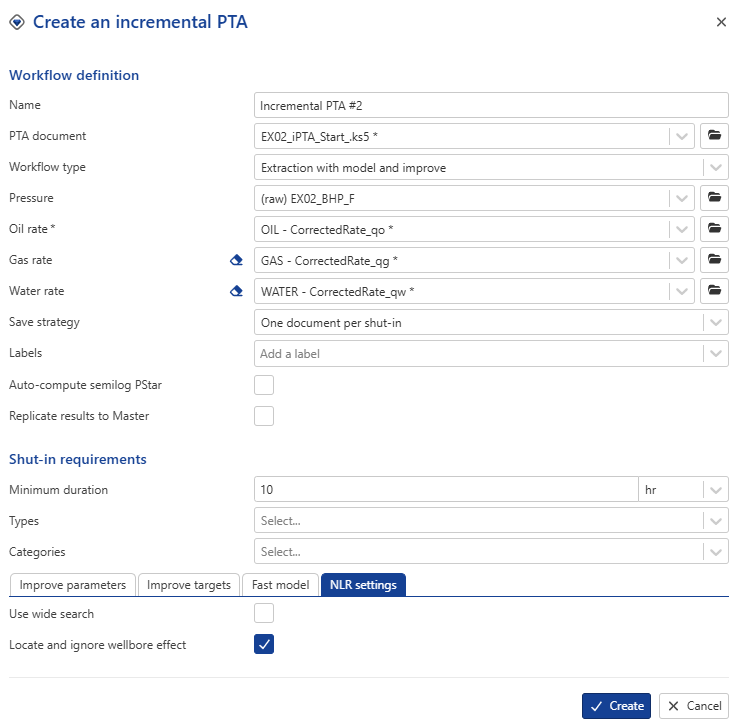
Name: this is a required field. Users can give whatever name they wish. For this session, let’s keep the default.
PTA document: This is the seed document for iPTA. Model parameters will be picked up from this Saphir file. Since the iPTA was called after selecting the Saphir file, EX02_iPTA_Start.ks5 is already selected. Leave the selection as is.
Pressure: The pressure gauge to use for iPTA. Switch this to (raw) EX02_BHP_F.
Oil, Gas and Water rates: Leave the default.
Defining iPTA Strategy
Save Strategy
There are two ways users can create/update Saphir files with new data:
Single document with one analysis per shut-in: any new data are sent to the PTA document defined in the iPTA creation wizard and a new analysis is created for each shut-in. A maximum of 10 analyses can be created in a single document, after which a new document will automatically be created.
One document per shut-in: Each shut-in is extracted in a new document. Data in each document are truncated at the extracted shut-in.
Workflow type
There are three types of iPTA workflows available:
Extraction only: This is the only available option if the selected PTA document does not contain a model. The data up to a given shut-in will be sent to the PTA µ-service which will perform the extraction.
Extraction with model: In addition to the steps explained in (1) above, the model in the ‘PTA document’ is extended up to the shut-in being processed.
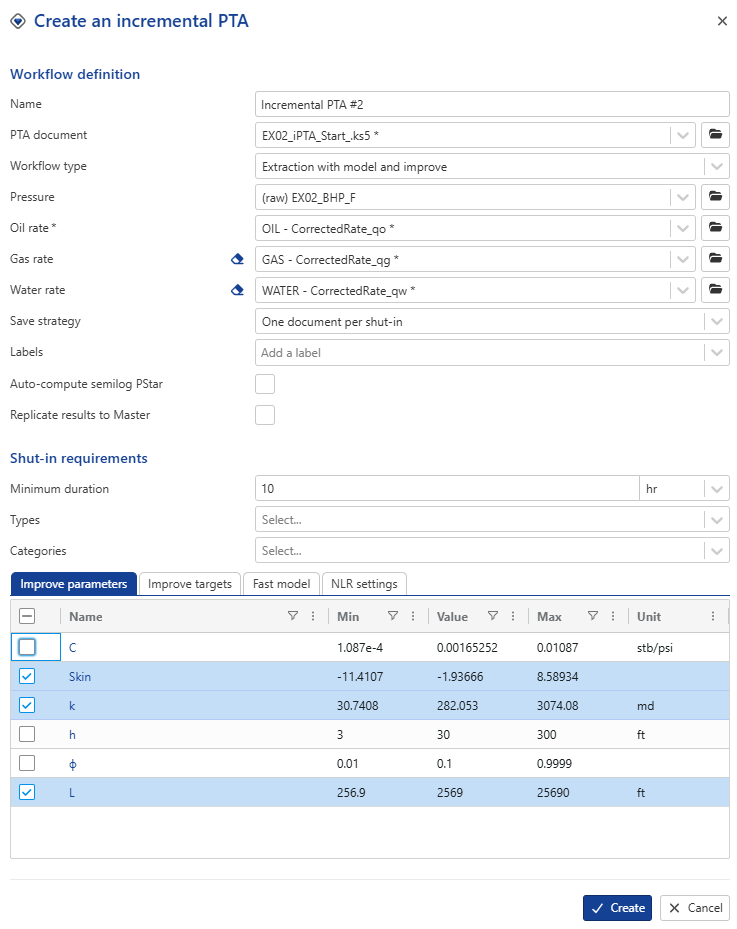
Extraction with model + improve: In addition to the steps explained in (2) above, if this option is selected, an improve strategy is requested by the user at the time of iPTA creation. The user can specify what model parameters to improve on, as well as their ranges. During execution, after the model has been extended to the processed shut-in, in improve on the loglog plot is performed.
For this session select the third option.
In the Improve parameters tab select to improve on model Skin, k_eq, and L. Select Replicate results to Master.
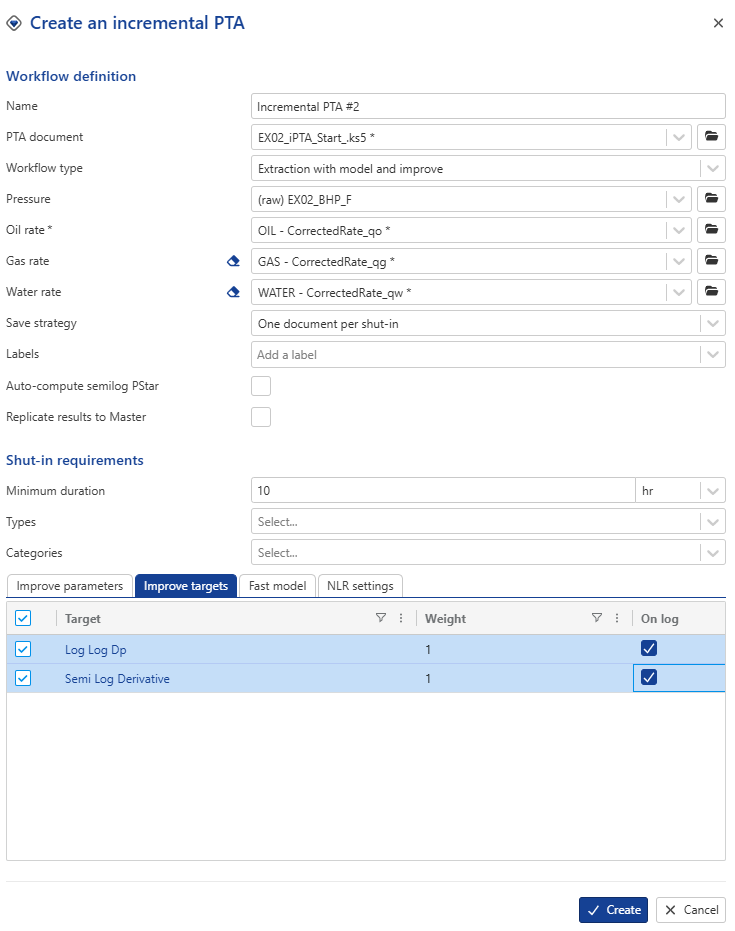
In Improve target tab, set the objective function to a 50/50 wight between Log-Log Δp and Semi-Log Derivative, and check the option On log.
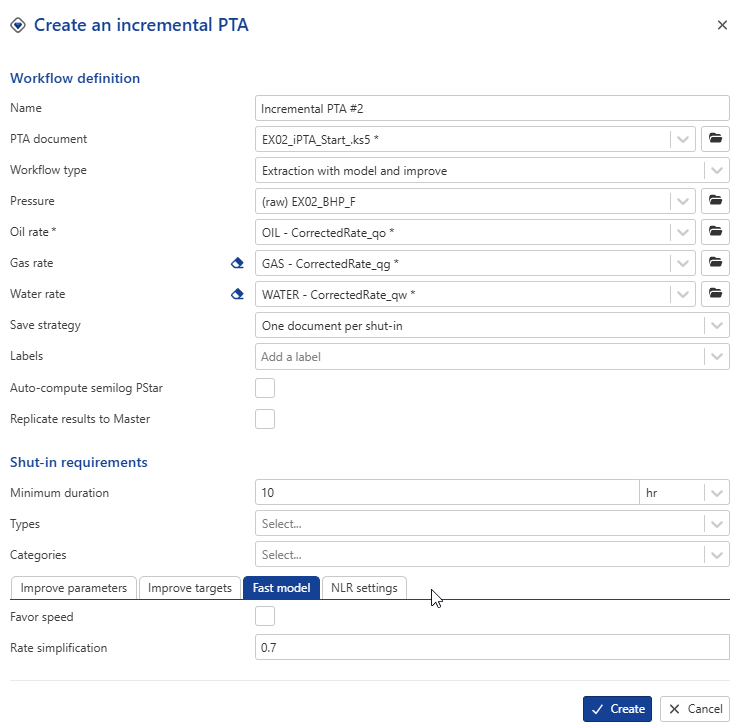
In the Fast model tab, leave it unchecked, as we will not use it for this example.
In NLR settings tab, check Locate and ignore wellbore effect. This option automatically removes the wellbore storage portion from the objective function, provided the algorithm successfully detects the end of the wellbore storage period.
|
| ||
|
|
Click on Create.
Viewing iPTA results
When an iPTA is first launched, it will create a new container under Well properties node in the field hierarchy, named Container for <<Name>>. A new folder called Workflows will also be created in the field hierarchy, with the iPTA and any files created by this iPTA listed there:
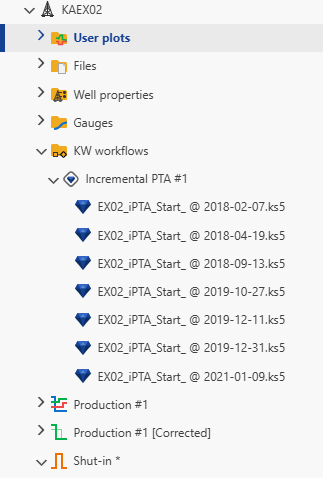 |
iPTA Results under Workflows
As the iPTA runs, each shut-in is sent to the PTA µ-service, which performs the extraction, generates the model, improves on the model and then saves a new file under the Incremental PTA #1 (or whatever name was given to the iPTA) node.
The document name follows this logic: <<Seed file name>> - <<start of shut-in date>>
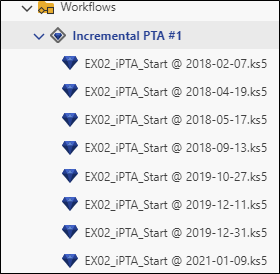 |
The process continues till the last available shut-in and then goes on standby listening for the next SI to become available.
Select any file under this node, go to plot tab and compare the loglog match for the different shut-ins:
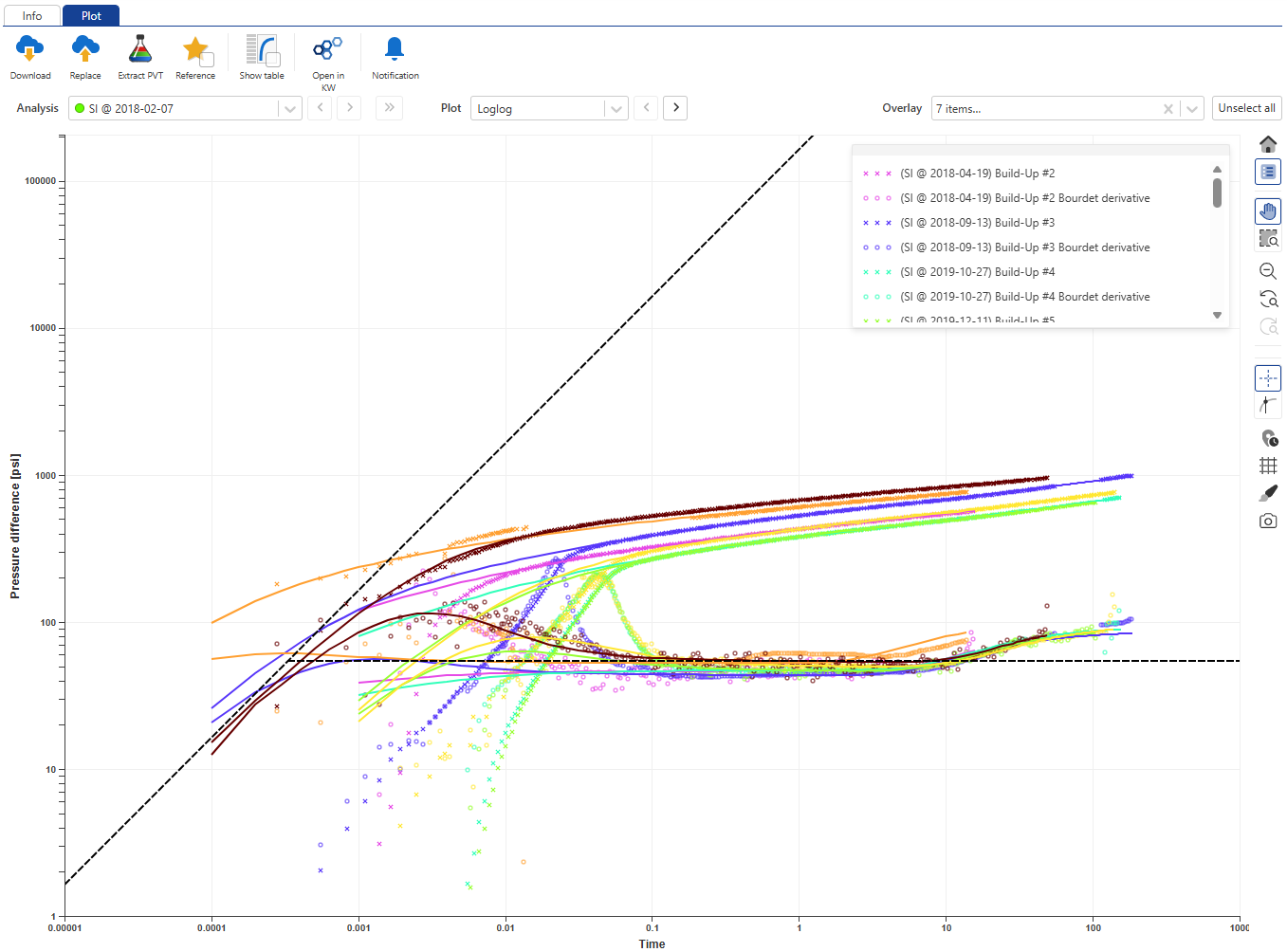 |
iPTA Results under Well properties
The contents under the Container for Incremental PTA #1 container are like those under the Master container. They will automatically be updated/appended as new shut-ins are processed, giving users a complete time-lapsed view of the different well properties.
Create a new User Plot under the well and call it PI, k S. Select Productivity Index, Permeability and Skin under Master container:
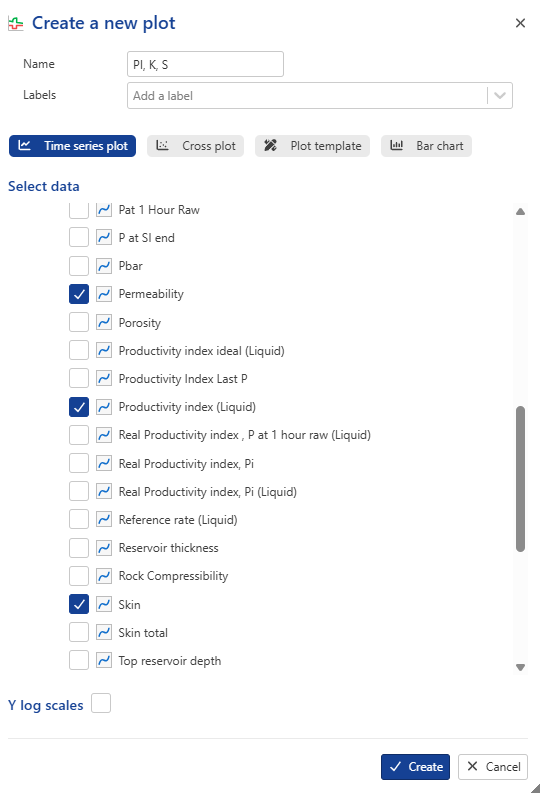 |
Click on Create:
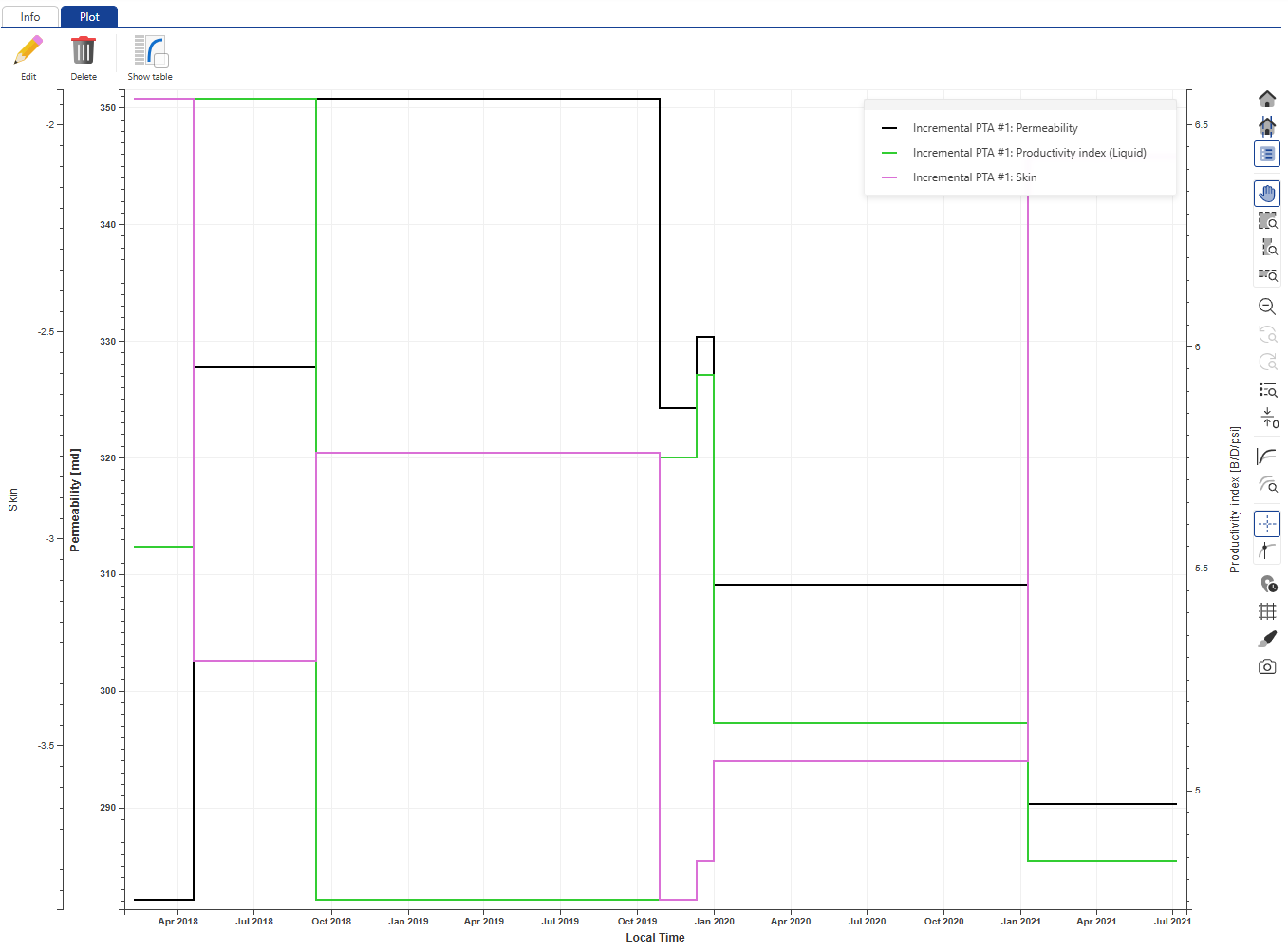 |
Introduction
Functions are the easiest way to process data channels in K-A. They allow creating new data sets that are the user-defined functions of any number of input sets of data.
The principle of working with the Function is to first define a function in the Automation mode and then create as many function instances as necessary for any well in PDG mode. Functions fall under the two categories:
Built-in functions
Custom functions
This session will use the built-in GOR and WC functions. Custom functions will be explored in the Data typing and Labels session.
Accessing available functions
Select the KAEX02 well in the field hierarchy and click on Function,  , under the Info tab:
, under the Info tab:
 |
In the consequent dialog, select GOR [Built-in] from the dropdown menu:
 |
This will launch the following dialog:
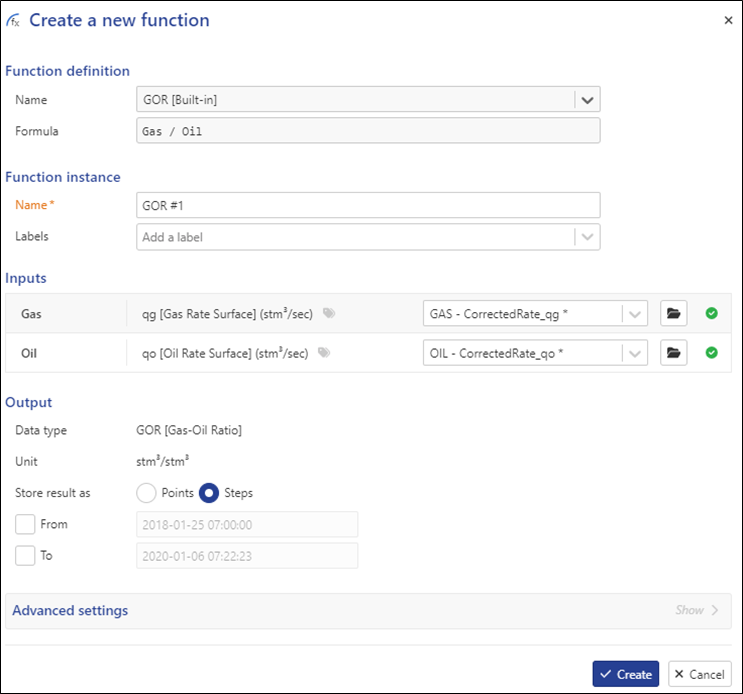 |
Click on Create.
Repeat the process to create a Water Cut channel. The two functions will appear under a new Functions folder in the field hierarchy:
 |
Click on GOR #1 in the field hierarchy and toggle to the plot tab:
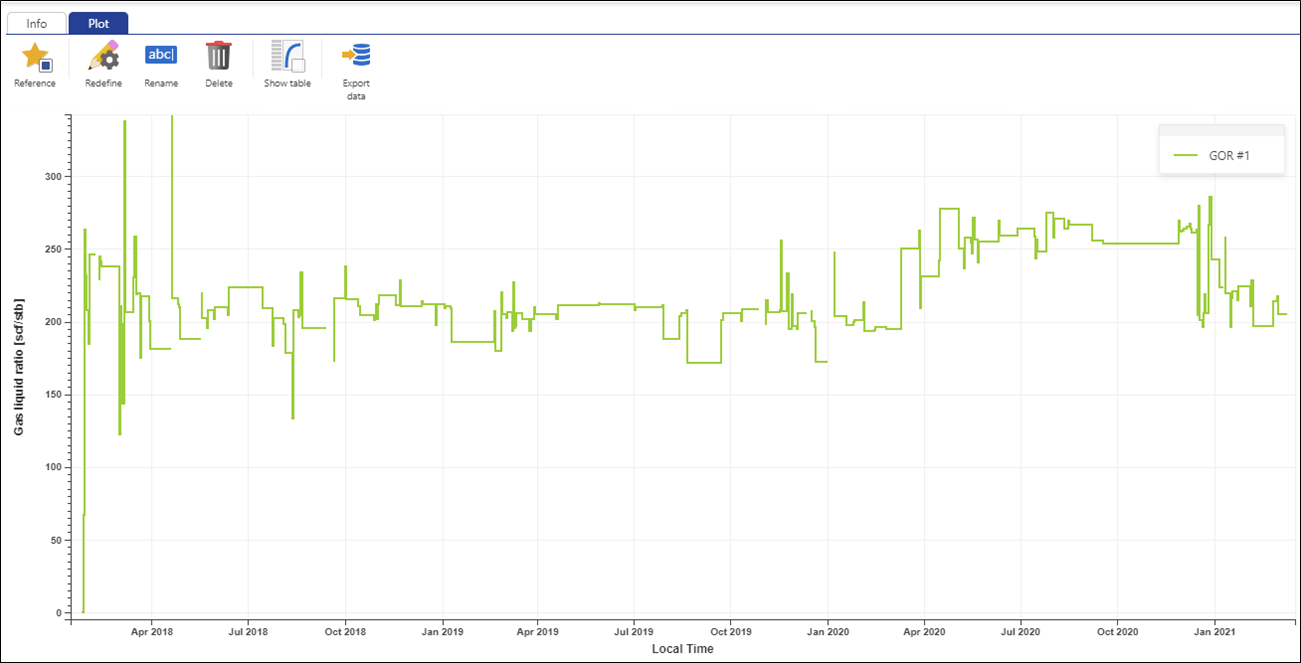 |
View the computed water cut gauge in the same manner.
Introduction
Plot templates can be created at the global K-A level, at the Field, Well Group and Well level. These provide a default view of the data at the selected level in the hierarchy. Plot templates benefit for data typing and labeling, which offer a flexible way to customize data display/visualization.
Applying/Editing template at field level
Select field node and go to the Plot tab.
 |
Click on Set template, . This will open the definition plot template instance applied to the field.
. This will open the definition plot template instance applied to the field.
Click on Load template
 |
Select Pressure and production which represents the default template
 |
Press Ok:
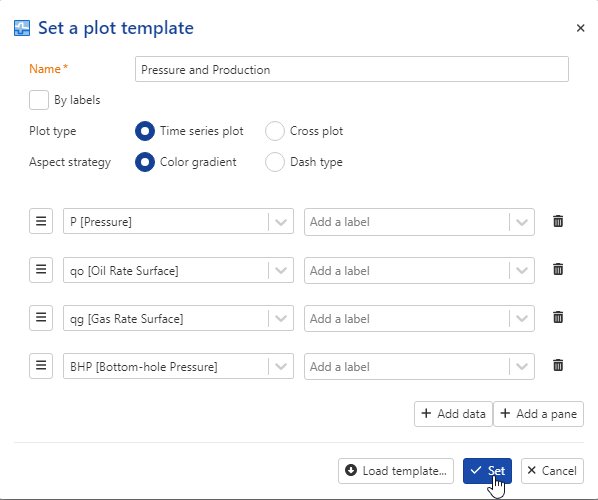 |
Now we see the pressure gauges in addition to the rate gauges.
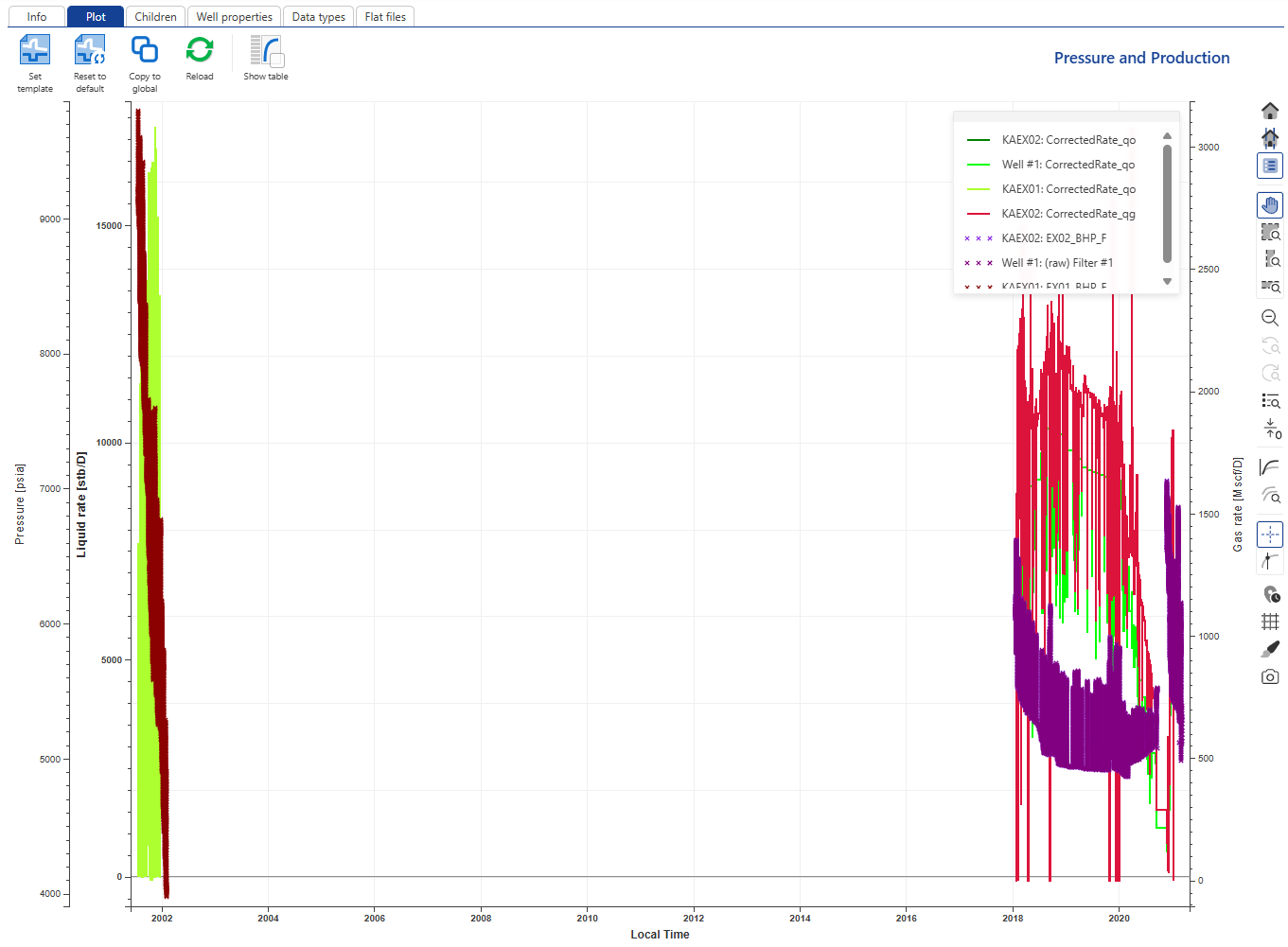 |
Let us make the field level plot a little clearer. Click on Set template,  . Click on Add a pane and in Pane 2, select BHP. Remove BHP from Pane 1.
. Click on Add a pane and in Pane 2, select BHP. Remove BHP from Pane 1.
Add a new pane and select to display GOR and WC in the third pane.
Add a fourth pane with the SI channel.
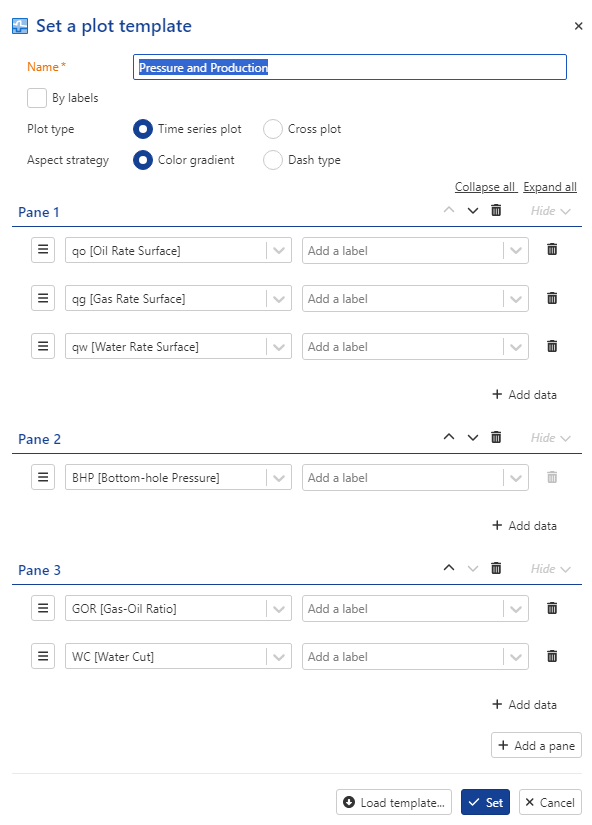
Note
All these changes are applied to the instance of the plot template. The original template definition is not affected and it is possible to reset back to it if needed by clicking on Reset default template , .
.
Applying/Editing template at Well level
Select KAEX02 well in the field heirarcy and click on Set template,  . Keep BHP in pane 1. Add a new pane and add oil rate, GOR and WC. Add a third pane.
. Keep BHP in pane 1. Add a new pane and add oil rate, GOR and WC. Add a third pane.
Click on  and select well property.
and select well property.
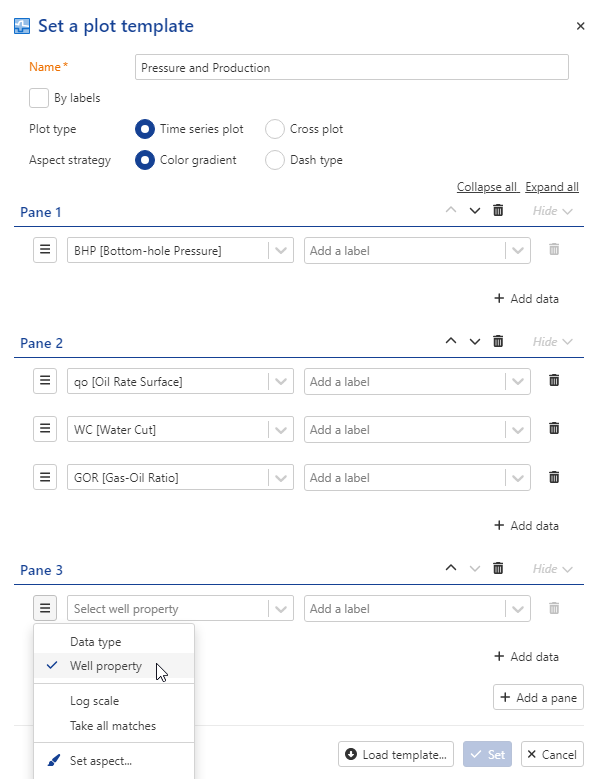
Add permeability
Repeat the steps to add skin:
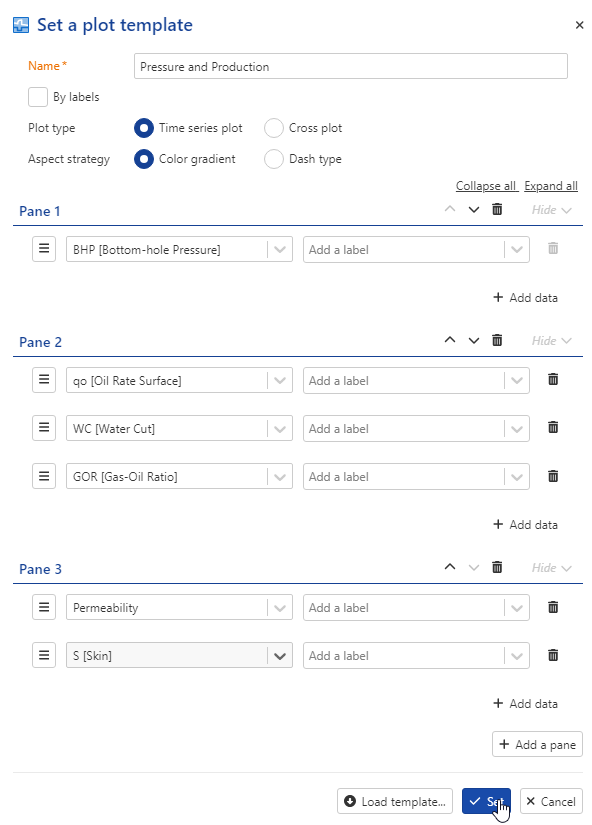
Press Set
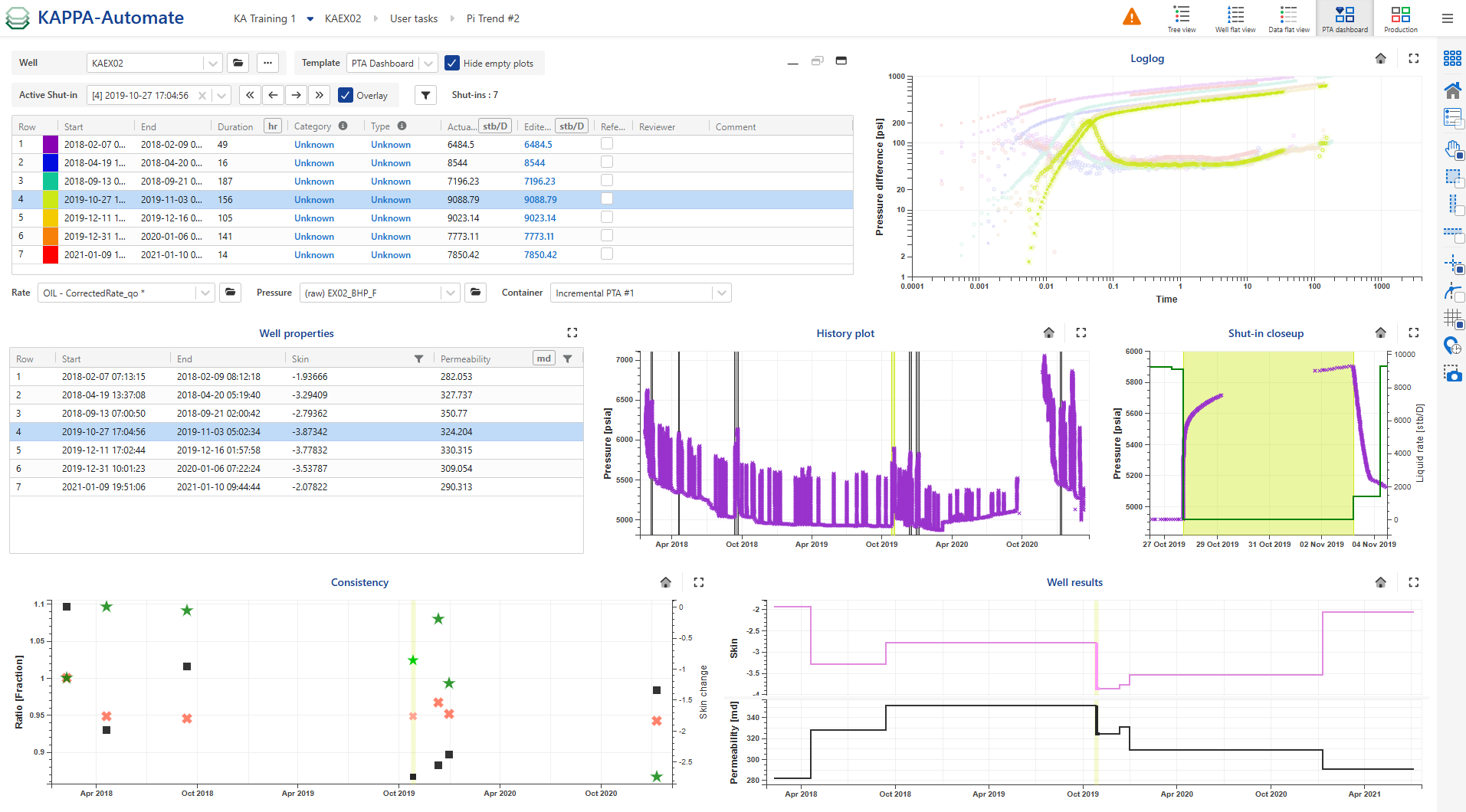
The PTA Dashboard provides users with a comprehensive, quick, and detailed view of the selected well, enabling them to monitor its performance over time. It is also useful in the PDG (Permanent Downhole Gauge) workflow, particularly for shut-in quality control. In this mode, users can visualize various data through plots, including history plots, detected shut-in events, corrected productions, and pressure. Additionally, users can easily navigate between wells within the field, examining information related to shut-ins, pressure, and production rates.
In the PTA dashboard users can:
View all validated shut-ins.
Set the reference shut-in.
Categorize shut-ins using attributes
Manually correct the rates prior shut-ins
Add PTA Dashboard template:
Go to KA home page by clicking KAPPA-Automate icon ,
 , at the top left.
, at the top left.Select Automation mode ,
 , in the main ribbon at the top
, in the main ribbon at the top
In the left panel, choose Plot templates, then switch to the Dashboard templates Tab.
Click on Create and name your template, for instance, PTA Dashboard.
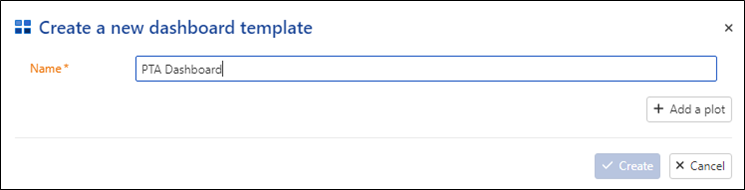
Click on Add a plot and follow these steps for each plot:
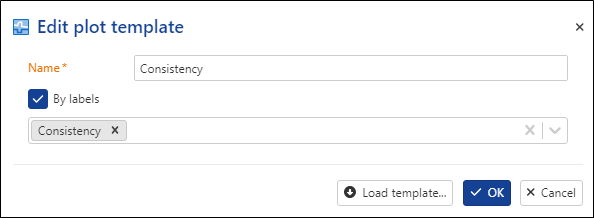
First plot: select By labels, name it Consistency, and the same name for the labels then click on OK. This will display the plot result generated by Consistency check user task.
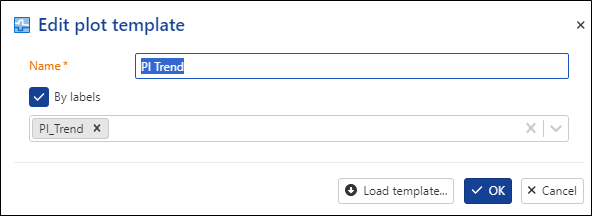
Second plot: select By labels, name it PI Trend, and add the PI_Trend label then click click on OK. This will display the histograms generated by the Productivity Index user task.
Third plot: Name it Well results, select Time series plot, Click on ,
 , select Well property, and select Skin from the dropdown list.
, select Well property, and select Skin from the dropdown list.Add a new pane and this time add Permeability.
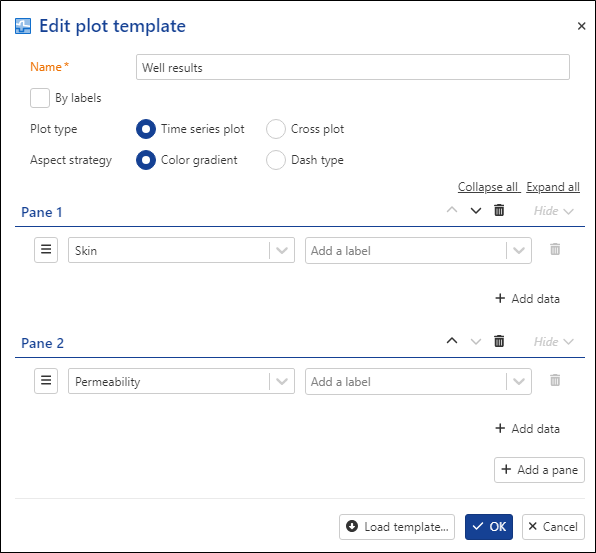
Click on Ok to create the template
PTA Dashboard
To access the PTA Dashboard:
Select well KAEX02 in the field hierarchy.
Click on PTA Dashboard ,
 , in the top right toolstrip.
, in the top right toolstrip.
By default, three plots are displayed (Zoom on Shut-in, History plot and Loglog plot).
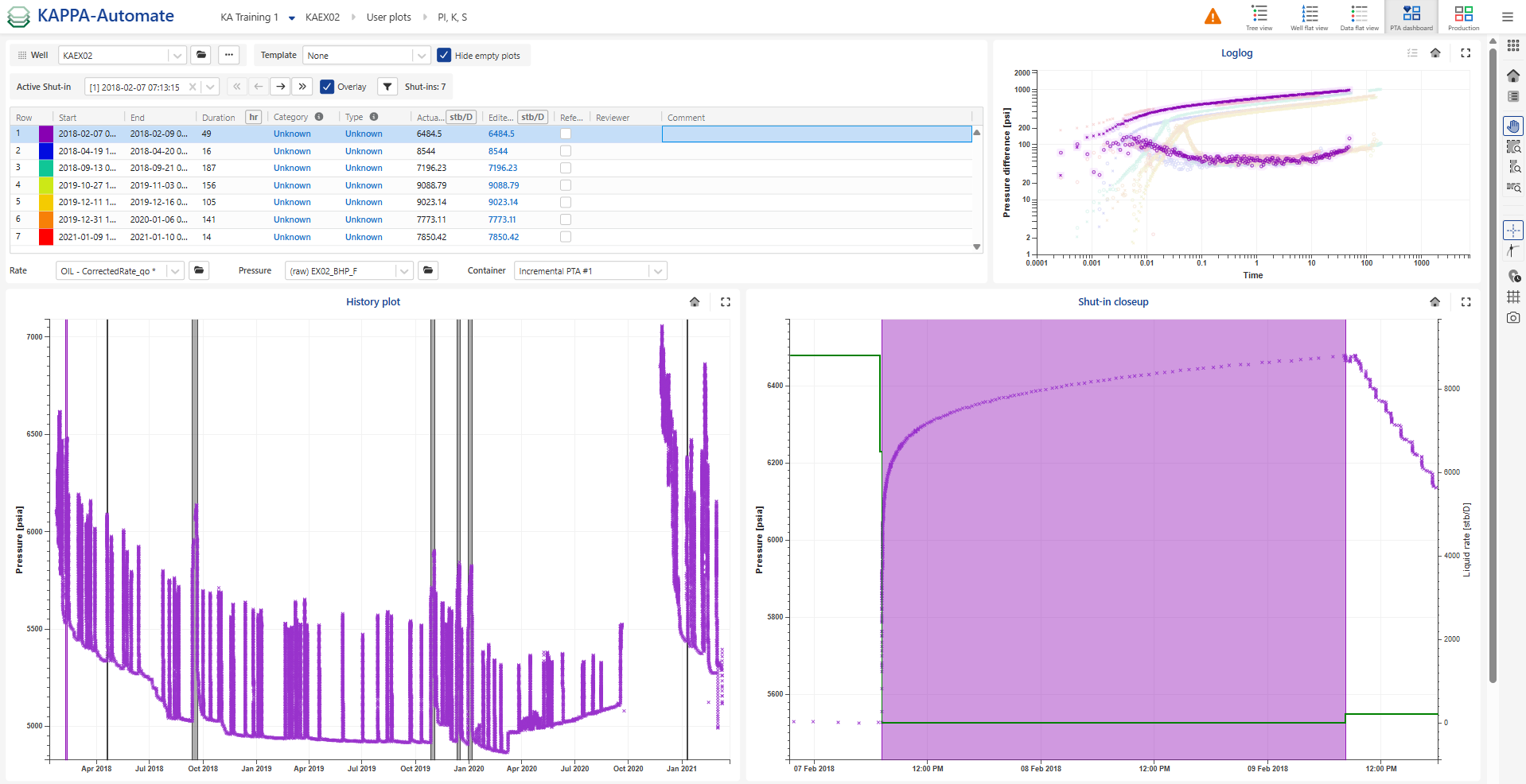
Use the Template drop down to select the PTA Dashboard template. All the data and results for the well can be viewed in a single page, enabling a consolidated analysis.
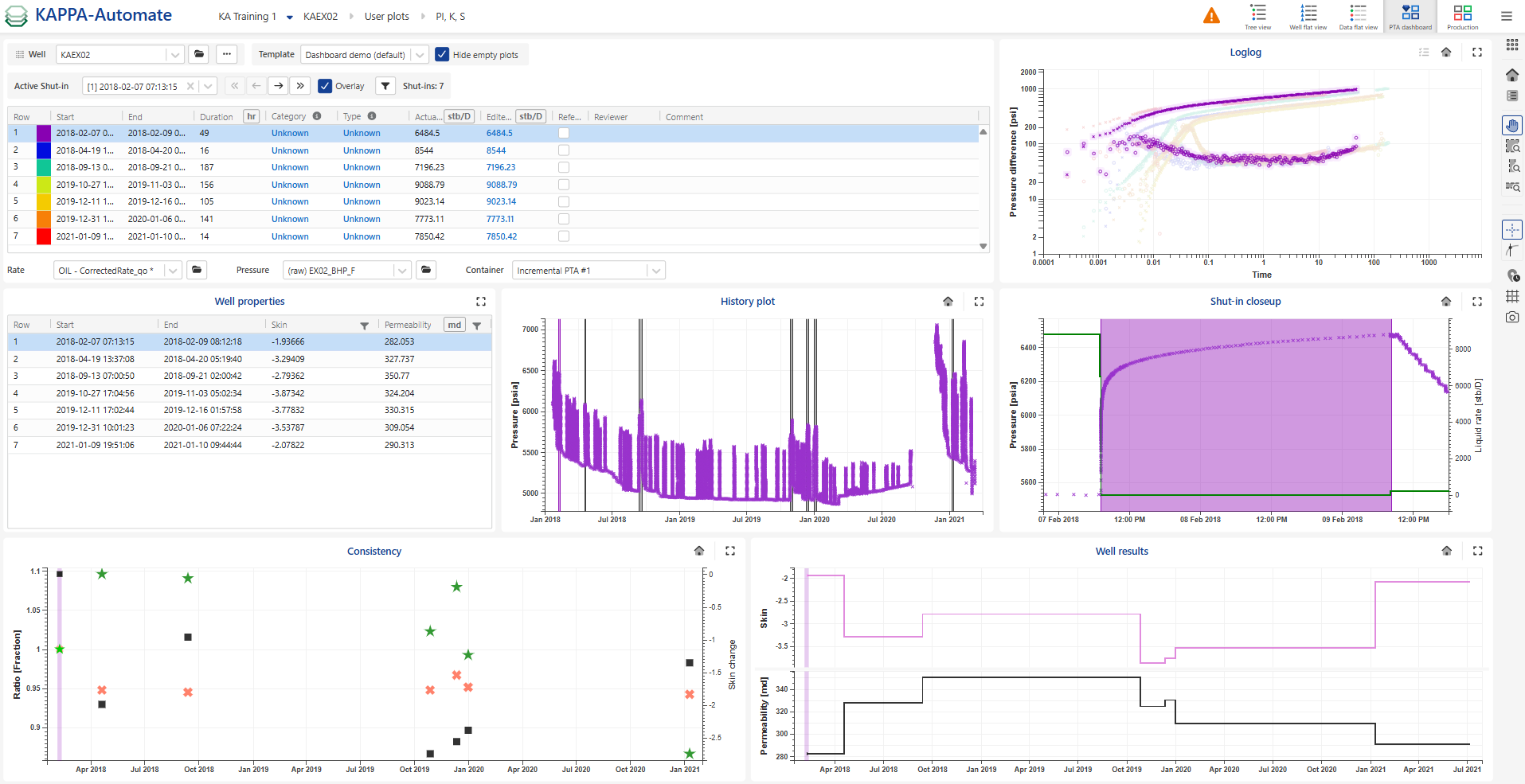
The table lists all the validated shut-ins along with multiple attributes for each. These include:
Category: users can choose from fit for use, not fit for use or unknown
Type: users can select from hard, soft or unknown
Reviewer: user who made the last change to any of attributes.
Reference shut-in: useful in several process for instance consistency check
Comment
Actual rate
Edited rate: Allows adjustment of the last rate step value before shut-in to address rate allocation issues. This adjustment vertically shifts the log-log plot on the fly.
For example, the last two shut-ins (SIs) are inconsistent with others, this may indicate an error in the rate computation. Edit the rates and see the immediate effect:
Edit the rate to 3000 and 10000 respectively for SI numbers 10 and 11.
Click Save,
 , to view the final results.
, to view the final results.